Greenhouse
(Green house, Green-house)
See also: Conservatory, Hothouse, Nursery, Orangery
History
The term greenhouse designated a plant-keeping house built to protect tender plants from cold weather. Although these structures were most commonly referred to as greenhouses, the terms “conservatory,” “glasshouse,” and “hothouse” were often used synonymously. Attempts were made to distinguish among the terms. According to Bernard M’Mahon (1806), for example, plants were planted in free soil and in “beds and borders” in a conservatory, whereas in a greenhouse, plants were kept in pots or tubs. A. J. Downing later wrote that plants were kept in the greenhouse until they were ready to be displayed in the conservatory. In actual usage, however, the terms were often used interchangeably. “Hothouse” or “stove” was also used to describe that part of the greenhouse with higher temperatures (see also Conservatory, Hothouse, and Orangery).
Although plant-keeping structures have been built since antiquity, the modern greenhouse, in which light and temperature could be artificially controlled, was possible only after 1700 when glassmaking improved and glass became cheaper [Fig. 1]. In addition to blowing glass, a pouring process was used by manufacturers. The earliest plant houses, which were called greenhouses in this country, had façades with large window openings that were integrated into a masonry, wood, or stone structure [Fig. 2]. These early buildings were replaced by iron-and-glass houses around the turn of the nineteenth century, which revolutionized greenhouse construction by allowing wide-span and filigree structures that let in more light. [1]
Greenhouse construction, evident as early as John Bartram’s 1739 description of Westover, Va., on the James River, continued through the mid-nineteenth century at sites ranging from elite houses such as Mount Clare, Charles and Margaret Tilghman Carroll’s plantation in Baltimore, to the more modest dwelling and greenhouse advertised for sale in Charleston in 1748. The pervasiveness of the structure reflects an interest in keeping exotic plants, which was a fundamental function of a greenhouse. In addition, the greenhouse allowed the extension of the growing season by providing a supportive environment for starting seeds, ripening fruit, and forcing flowers.
Two major concerns in greenhouse design were the admission of light and the creation of artificial heat. These problems could be solved in the modest construction of a building with a high back wall, a low front wall, and a glazed roof above, as shown in the greenhouse at Kirk Boott’s residence in Boston [Fig. 3]. The brick wall of a greenhouse could also serve as support for trellises or espaliered fruit trees. Most simple greenhouses built in this mode did not require the high temperatures or moist atmosphere of hothouses. As M’Mahon pointed out in 1806, such a greenhouse needed only enough artificial heat to “keep off frost and dispel damps,” whereas the hothouse required an inside stove and more glass (see Conservatory and Hothouse for further discussion of heating systems).
Early greenhouses had brick, stone, or dirt floors, but improved designs later made use of wood floors so that the air space under the floor might allow hot air to radiate under the entire floor. [2] A. J. Downing recommended a small, air-tight coal stove and the related Polmaise mode of heating. This heating technique was based on the recirculation of air in the greenhouse: cold air was drawn into a furnace and heated air was expelled into the farthest reaches of the structure. [3] In 1848, Downing described a plant house for Montgomery Place on the Hudson River that utilized this feature.
Texts
Usage
- Bartram, John, July 18, 1739, describing Westover, seat of William Byrd II, on the James River, Va. (1992: 121) [4]
- “Col Byrd is very prodigal in Gates roads walks hedges & seeders [cedars] trimed finely & A little green house with 2 or 3 [orange] trees . . .”
- Smith, John, 1745, describing Springettsbury, near Philadelphia, Pa. (quoted in Weber 1996: 46–47) [5]
- “In the afternoon, the weather being so agreeable, John Armitt and I rode to Charles Jenkin’s ferry on Schuykill. We ran and walked a mile or two on the ice. On our way thither we stopped to view the proprietor’s green-house, which at this season is an agreeable sight; the oranges, lemons and citrons were, some green, some ripe, some in blossom.”
- Anonymous, 1748, describing in the South Carolina Gazette a property for sale in Charleston, S.C. (quoted in Lounsbury 1994: 167) [6]
- “[The dwelling house contains] a large Garden, with two neat Green Houses for sheltering exotic Fruit-Trees, and Grape-Vines.”
- Fisher, Daniel, 1755, describing the greenhouse in the Proprietor’s Garden, Philadelphia, Pa. (quoted in Martin 1991: 211) [7]
- “What to me surpassed every thing of the kind I had seen in America was a pretty bricked Green House, out of which was disposed very properly in the Pleasure Garden, a good many Orange, Lemon and Citrous [sic] Trees, in great profusion loaded with abundance of Fruit and some of each sort seemingly then ripe.”
- Redwood, Abraham, Jr., c. 1760, in a letter to his plantation manager, describing Redwood Farm, seat of Abraham Redwood, Jr., Portsmouth, R.I. (Rhode Island Landscape Survey)
- “I would desire you send to me one hhd of good rum and one hhd of good sugar and I desire that you speak to your overseer to put up in Durt one dozen of Small orange Trees that has bore one or two years with the young fruit upon them, if to be had that has bore two or three years of Saffadella trees, four young figg trees and some Guavas roots, to put in my greenhouse, for I have made a garden of 1 1/2 acres of land and I have built a green house twenty-two feet long, Twelve feet wide and Twelve feet high, and a hotte house Sixteen feet long Twelve feet wide and Twelve feet high, and I have growing in my greenhouse Fifty young fruit trees from six inches to four feet high, and my Gardner says ye largest will not bear fruit these two years, and I have hotte house Strawberries, Bush beans and Crownations in Blossom.”
- Bartram, John, June 24, 1760, in a letter to Peter Collinson, describing his plans for the Bartram Botanic Garden and Nursery, vicinity of Philadelphia, Pa. (quoted in Darlington 1849: 224) [8]
- “Dear friend, I am going to build a greenhouse. Stone is got; and hope as soon as harvest is over to begin to build it, to put some pretty flowering winter shrubs, and plants for winter’s diversion; not to be crowded with orange trees, or those natural to the Torrid Zone, but such as will do, being protected from frost.”
- Anonymous, c. 1765, describing the greenhouse and garden of Dr. Upton Scott, Annapolis, Md. (quoted in Sarudy 1989: 149) [9]
- “He is fond of botany and has a number of rare plants and shrubs in his greenhouse and garden.”
- Ambler, Mary M., 1770, describing Mount Clare, plantation of Charles and Margaret Tilghman Carroll, Baltimore, Md. (1937: 166) [10]
- “took a great deal of Pleasure in looking at the Bowling Green & also at the Garden which is a very large Falling Garden there is a Green House with a good many Orange & Lemon Trees just ready to bear besides which he is now buildg [sic] a Pinery where the Gardr expects to raise about an 100 Pine Apples a Year He expects to Ripen some next Sumer.”
- Washington, George, August 11, 1784, in a letter to Tench Tilghman, describing Mount Vernon, plantation of George Washington, Fairfax County, Va. (quoted in Johnson 1953: 95–96) [11]
- “I shall essay the finishing of my green house this fall, but find that neither myself, nor any person about me is so well skilled in the internal construction as to proceed without a probability at least of running into errors.
- “Shall I for this reason, ask the favor of you to give me a short description of the Green-house at Mrs. Carrolls Mount Clare, plantation of Charles and Margaret Tilghman Carroll, Baltimore, Md.]? I am persuaded, now that I planned mine upon too contracted a scale. My house is (of Brick) 40 feet by 24, in the outer dimensions, and half the width disposed of for two rooms, back of the part designed for the green house; leaving the latter in the clear not more than about 37 by 10.”
- Tilghman, Tench, August 18, 1784, in a letter to George Washington, describing Mount Clare, plantation of Charles and Margaret Tilghman Carroll, Baltimore, Md. (quoted in Trostel 1981: 77) [12]
- “Inclosed you will find answers to your Several Queries respecting the Green House including the order in which they were put, and that you may better understand the Construction of Mrs Carroll’s, I have made a rough Plan of the Manner of conducting the Flues—Your Floor being 40 feet long Mrs Carroll recommends two Flues to run up the Back Wall, because you may then increase the number of Flues which run under the Floor, and which she looks upon as essential—The trees are by that means kept warm at the Roots—She does not seem to think there is any occasion for the Heat to be conveyed all around the Walls by means of small Vacancies left in them She has always found the Flues mark’d in the plan sufficient for her House—
- “She recommends it to you to have the upper parts of your Window sashes to pull down, as well as the lower ones to rise—you then Give Air to the Tops of your Trees—
- “Your Ceiling she thinks ought to be Arched and at least 15 feet high—She has found the lowness of hers which is but 12 very inconvenient—
- “Smooth Stucco she thinks preferable to common Plaster because drier—
- “The Door of the House to be as large as you can conveniently make it—otherwise when the Trees come to any size, the limbs are broken and the Fruit torn off by moving in and out
- “It is the Custom in many Green Houses to set the Boxes upon Benches—But Mrs Carroll says they do better upon the Floor, because they then receive the Heat from the Flues below to more advantage—
- “I recollect nothing more—I hope your Excellency will understand this imperfect description of a matter which I do not know much about myself.”
- Cutler, Rev. Manasseh, July 14, 1787, describing Gray’s Tavern, Philadelphia, Pa. (1888: 1:275) [13]
- “We returned to the grass plat, from which we ascended several glaces by a serpentine gravel walk, and came to the Green-house. It is a very large stone building, three stories in the front and two in the rear. The one-half of the house is divided lengthwise, and the front part is appropriated to a green-house, and has no chamber floors. It is finished in the completest manner for the purpose of arranging trees and plants in the most beautiful order. The windows are enormous. . . .We then took a view of the contents of the greenhouse, beautifully arranged in the open air on the south of the garden. Here were most of the trees and fruits that grow in the hottest climates. Oranges, lemons, etc., in every stage from blossoms to ripe fruit; pine-apples in bloom, and those that were fully ripe. The flowers were numerous and extremely fragrant.”
- Brissot de Warville, J.-P., 1788, describing Mount Vernon, plantation of George Washington, Fairfax County, Va. (1792: 427–28) [14]
- “I hastened to arrive at Mount Vernon. . . . On this rout traverse a considerable wood, and after having passed over two hills, you discover a country house of an elegant and majestic simplicity. It is preceded by grassplats; on one side of the avenue are the stables, on the other a greenhouse, and houses for a number of negro mechanics.”
- Barrell, Joseph, October 19, 1793, in a letter to W. W. Pringle, ordering plants for Pleasant Hill, seat of Joseph Barrell, Charlestown, Mass. (quoted in Hammond 1982: 230) [15]
- “[Ten half standard and ten espaliered Morella cherry trees] to cover the back of my greenhouse. . . . I want a (new) person that understands green house plants & laying out grass plots & grounds, you will send the trees by the same opportunity the gardener comes that he may attend them on the passage.”
- Médéric Louis Élie Moreau de St.-Méry, March 26, 1797 (quoted in Roberts 1947: 240) [16]
- "I went... to visit Robert Morris’s greenhouse [serre chaud] near Philadelphia. It had very beautiful specimens of orange trees, lemon trees, and pineapples.]
- "A Schedule of Property within the State of Pennsylvania Conveyed by Robert Morris, to the Hon. James Biddle, Esq. And Mr. William Bell, in Trust for the use and account of the Pennsylvania Property Company," c. September 6, 1797 [17]
- "An Estate called the Hills Situate in the Northern Liberties, near the City of Philadelphia, containing Three hundred acres of land highly improved, and on which are erected a large and elegant greenhouse, with a hot house of fifty feet on each side; on the back front a House for a gardener, with one large and five small rooms, also two large rooms on the back or north front of the hot house, with an excellent vault under the green houses, and a covered room for preserving roots & c in winter; the whole being a strong stone building, with the necessary glasses, casements, fruit trees, plants shrubs & c in good order; a well of excellent water, with a pump close to the north front the whole enclosed within a large Garden stocked with fruit trees of the best kind &c. & c."
- Booth, William, 23 September 1799, advertisement in the Federal Gazette and Baltimore Daily Advertiser (quoted in Sarudy 1989: 115) [9]
- “TO BOTANISTS, GARDENERS AND FLORISTS, and to all other gentlemen, curious in ornamental, rare exotic or foreign plants and flowers, cultivated in the greenhouse, hot-house, or stove, and in the open ground. A large and numerous variety of such rarities is now offered for sale. . . .
- “After reserving a general and suitable stock, he has to spare a well assorted and great variety of those things, comprising a beautiful collection, sufficient to decorate, furnish, and ornament a spacious or handsome greenhouse at once. . . . The whole is a truly valuable collection, such as is very rarely to be met with for sale on this side of the Atlantic—indeed a moiety of them would comprise a very desirable and exclusive variety, consisting of many or most of the tropical fruits, and other rare and curious finely ornamental trees, scrubs and plants; with a numerous and abundant assortment of choice bulbous, tubrous, and fibrous rooted flowering and ornamental plants in mixtures . . . for which . . . please apply to John Cummings, at the alms-house, Messrs. David and Cuthbert Landrith, gardeners and nursery-men. . . .
- “N.B. it is now a good time and proper season to build a green-house, and to remove plants.”
- Codman, Dr. John, August 24, 1800, describing the Grange, estate of Dr. John and Sarah Codman, Lincoln, Mass. (quoted in Hammond 1982: 170) [15]
- “behind which are stables (and) servants houses of various kinds, & in particular the gardens and greenhouses all of which are thus covered from sight . . . retirement is the object in this country. To be alone in the world as Adam and Eve were seems to be the taste, and the calm soft sweet scenes to be desirable.”
- Southgate, Eliza, July 6, 1802, describing Elias Hasket Derby Farm, Peabody, Mass. (quoted in Kimball 1940: 76) [18]
- “We returned to the house, which was neat and handsome, and from thence visited the green house, where we saw oranges and lemons in perfection . . . every plant and shrub which was rare and beautiful was collected here.”
- Cutler, Rev. Manasseh, November 22, 1803, describing the Woodlands, seat of William Hamilton, near Philadelphia, Pa. (1888: 2:145) [19]
- “We then took a turn in the gardens and the green-houses. In the gardens, though ornamented with almost all the flowers and vegetables the earth affords, I was not able to walk long. The green-houses, which occupy a prodigious space of ground, I can not pretend to describe. Every part was crowded with trees and plants from the hot climates, and such as I had never seen, all the spices, the tea-plant in full perfection; in short, he assured us there was not a rare plant in Europe, Asia, or Africa, many from China and the islands in the South Seas, none, of which he had obtained any account, which he had not procured.”
- Anonymous, November 25, 1805, describing the Museum Naturae, Norfolk, Va. (Norfolk Gazette and Publick Ledger)
- “MUSEUM NATURÆ, of Norfolk and Portsmouth . . .
- “Botanical Garden, containing specimens of all the vegetable productions of this country, and furnished with green-houses, for all such exotick and rare plants, as may be procured from abroad.”
- Boott, Kirk, April 15, 1806, describing the residence of Kirk Boott, Boston, Mass. (quoted in Emmet 1996: 35) [20]
- “my Greenhouse has flourished beyond my expectation, and what pleases me much, I have found my skill equal to the care of it. Lettuces in abundance I have preserved, and have had fine Sallads thro’ the Winter.”
- Hosack, David, 1806, describing Elgin Botanic Garden, New York, N.Y. (pp. 3–4) [21]
- “In the year 1801 I purchased, of the Corporation of the city of New-York, twenty acres of ground; the greater part of which is now in cultivation. Since that time, a Conservatory, for the more hardy green-house plants, has been built.”
- Jefferson, Thomas, March 1, 1808, in a letter to William Randolph, describing Monticello, plantation of Thomas Jefferson, Charlottesville, Va. (1944: 366) [22]
- “my green house is only a piazza adjoining my study, because I mean it for nothing more than some oranges, Mimosa Farnesiana & a very few things of that kind. I remember to have been much taken with a plant in your green house, extremely odoriferous, and not large . . . (Jefferson Papers, L. C. [Library of Congress]).”
- Joseph Newton, Arthur Smith, John E. West, and Timothy B. Crane, 1810, describing the Elgin Botanic Garden, New York, N.Y. (quoted in Hosack 1811: 45) [23]
- “Estimate of the Buildings at the Botanic Garden.
- “We, the subscribers, builders, and residents of the city of New-York, at the request of doctor David Hosack, have valued the improvements on his land, near the four mile stone, called the botanic garden, to wit: the hot bed frames, the conservatory or green house, and its appendages, the dwelling house, the hot houses and their back buildings, the lodges, the gates and the fences around the land, including the wells, at the sum of twenty-nine thousand three hundred dollars.”
- Peck, William Dandridge, 1818, describing the Cambridge Botanical Garden, Cambridge, Mass. (quoted in Hammond 1982: 254) [15]
- “exotic plants, contributed by friends of the institution, who possessed greenhouses in the vicinity, who as they have acquired new plants, have generously continued to impart them.”
- Memorial of the Columbian Institute, December 1818, describing the Columbian Institute, Washington, D.C. (quoted in O’Malley 1989: 123) [24]
- “[ Columbian Institute lottery for] enclosing the grounds, for the erection of their hall—their laboratory—their hot and green houses,—their library and museum, and for the cultivation of the botanic garden, wherein they hoped ‘to soon present to the view of their fellow citizens specimens of all the plants of this middle region of our country, with others exotic and domestic . . . for the promotion of a great national object.’”
- Bryant, William Cullen, August 25, 1821, describing the Vale, estate of Theodore Lyman, Waltham, Mass. (1975: 108–9) [25]
- “He took me to the seat of Mr. Lyman. . . . It is a perfect paradise. . . . We visited the green-house. Here were pine apples gro[wing. T]he rafters were covered with the grape vine of Europe whose clusters were nearly ripe. —Here was an American aloe whose ensiform leaves are as thick and as large as I am—a species of datura with large white flowers of the size of a half pint tumbler—and a thousand other curious matters—”
- Peale, Charles Willson, c. 1825, describing Belfield, estate of Charles Willson Peale, Germantown, Pa. (Miller, Hart, and Ward, eds., 2000: 5:383) [26]
- “finding a spring stream in the Garden he followed it up the side of the hill, untill it become of some debth and among large Stones—and having at this place made a considerable cavity in the bank round the source of the Spring, to wall it up this hollow and arch it over, it was thought that it might be an excellent place to keep cabbage and Turnups &c during the winter season, but on tryal it was found to[o] moist and warm, for those vegetables sprouted and took a second groath, and they were obliged to take them out, in the first of January, and cover them with earth in the usial mode. This tryal gave the Idea of building a green house jouining to the arched cave—and that Green house keepted all exotic plants perfectly well without the aid of Stoves in the severest winters.”
- Anonymous, October 3, 1828, describing André Parmentier’s horticultural and botanical garden, Brooklyn, N.Y. (New England Farmer 7: 85)
- “The green-house department, although not so extensive as some in our vicinity, contains many beautiful plants exhibited with the same tasteful arrangement which characterizes the whole of Mr. Parmentier’s establishment; even the method in disposing the pots according to some principle of grouping or contrasting the color and size of the flowers, entertains the eve, and shows the variety of ways in which a skillful gardener may distribute his materials to produce picturesque effect.”
- Anonymous, December 31, 1828, describing in the Cincinnati Advertiser of the death of Mrs. Jackson (Hermitage Collections, John Trotwood Moore Papers)
- “Mrs. Jackson. . . . We have understood from verbal information that the origin of Mrs. Jackson’s disease was severe cold, caught in her greenhouse, while attending to her plants and flowers.”
- Committee of the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society, 1830, describing Lemon Hill, estate of Henry Pratt, Philadelphia, Pa. (quoted in Boyd 1929: 432) [27]
- “The treasures contained in the hot and green houses are numerous. Besides a very fine collection of Orange, Lemon, Lime, Citron, Shaddock, Bergamot, Pomgranate and Fig trees in excellent condition and full of fruit, we notice with admiration the many thousand of exotics to which Mr. Pratt is annually adding. The most conspicuous among these, are the tea tree; the coffee tree—loaded with fruit; the sugar cane; the pepper tree; Banana, Plantain, Guva, Cherimona, Ficus, Mango, the Cacti in great splendour, some 14 feet high, and a gigantic Euphorbia Trigonia—19 years old, and 13 feet high. The green houses are 220 feet long by 16 broad; exhibiting the finest range of glass for the preservation of plants, on this continent.
- “Colonel Perkins, near Boston, has it is true, a grapery and peach Espalier, protected by 330 feet of glass, yet as there are neither flues not foreign plants in them, they cannot properly be called green houses, whereas Mr. Pratt’s are furnished with the rarest productions of every clime, so that the committee place the conservatory of Lemon Hill at the very head of all similar establishments in this country.”
- Forman, Martha Ogle, October 12, 1830, describing Rose Hill, home of Martha Ogle Forman, Baltimore County, Md. (1976: 292) [28]
- “I rode out with Mrs. Longstreeth to her country seat. I was very much pleased they have a very spacious house handsomely furnished, an elegant green house and hot house and all the grounds in beautiful order.”
- Thacher, James, December 3, 1830, “An Excursion on the Hudson,” describing Hyde Park, seat of Dr. David Hosack, on the Hudson River, N.Y. (New England Farmer 9: 156)
- “At an equal distance south, is to be seen the green house and hot house, a spacious edifice, constructed with great architectural taste and elegance, and well calculated for the preservation of the most tender exotics that require protection in our climate. It is composed of a centre and two wings, extending 110 feet in front and from 17 to 20 feet deep. One apartment is appropriated to a large collection of pines.”
- Dearborn, H.A.S., 1832, describing Mount Auburn Cemetery, Cambridge, Mass. (quoted in Harris 1832: 65) [29]
- “On the southeastern and northeastern borders of the tract can be arranged the nurseries, and portions selected for the culture of fruit trees and esculent vegetables, on an extensive scale; there may be arranged the Arboretum, the Orchard, the Culinarium, Floral departments, Melon grounds, and Strawberry beds, and Green houses.”
- Logan, Deborah Norris, February 13, 1832, describing greenhouses in the vicinity of Philadelphia, Pa. (quoted in Weber 1996: 45) [30]
- “There is a Report of the Committee of the Horticultural Society . . . in which is displayed a great ignorance of the former taste for Gardening amongst us when it states, that Mr. Pepper’s Green house, originally built by the late Dr. Barbon, was the first Green house built in Pennsylvania; this is not So.—The Greenhouse at Sprigetsbury, built by Margaret Freame daughter of William Penn, was the first;—the one attached to the House of my Father [Charles Norris] . . . was the next; and to this was added a hot-house; with its bark-bed and roof of Glass, where upwards of 50 Pine-apples were raised of a Season, besides many rare plants.
- “My Father [in-law] Logan, had also a Green house in town, as well as a good one here [at Stenton], for he was an excellent Horticulturalist, and had many rare and beautiful Plants; indeed the large and fine Orange and lemon trees which now ornament Pratts Greenhouse at Lemon Hill were originally of his raising. . . . Israel Pemberton likewise had a Green House for his wife’s Amusement, and there was one at Fair-hill [home of Isaac Norris Jr.].”
- Hovey, C. M., February 1835, “Calls at Gardens and Nurseries,” describing Oakley Place, seat of William Pratt, Boston, Mass. (American Gardeners’ Magazine 1: 71)
- “Mr. Pratt’s greenhouse is entirely new, having been erected the last summer; it is heat[ed] with two brick flues, one only of which is used unless in very severe weather. The stage consists of one range running the whole length, with two tiers of shelves; one running up very steep from the walk, which runs parallel with the back wall, and the other from the front walk, about the same slope as the surface of the glass.”
- Hovey, C. M., July 1835, “Notices of some of the Gardens and Nurseries in the neighborhood of New York and Philadelphia” (American Gardeners’ Magazine 1: 241)
- “There is another class of gardens in Philadelphia, called public gardens, which combine in addition to a flower garden, green-houses, hothouses, &c., a bar-room or tavern; this latter addition we are far from believing useful or needful.”
- B., J., October 1, 1836, “Horticulture in Maine,” describing the garden of M. P. Sawyer, Portland, Maine (Horticultural Register 2: 380–81)
- “The garden of M. P. Sawyer, Esq. contains the only green-house of any note in the city or vicinity. This we visited, and found MR Milne, who has charge of it, a man well skilled in his profession, and an ardent admirer of flowers. There are two houses upon it—The first a cold house for peaches and grapes, fiftythree feet long. The trees and vines were planted in it about the 20th June, 1835. The peach and some other trees are trained to the wall in a fine manner, and will probably produce fruit another season. . . .
- “The other building is a common green-house or conservatory, fifty feet long, devoted in part to grapes.”
- Hovey, C. M., May 1837, “Notes on some of the Nurseries and Private Gardens in the neighborhood of New York and Philadelphia” (Magazine of Horticulture 3: 164–66)
- “Residence of ____ Perry, Esq.— . . .The house is built in the Grecian style, with a wing extending to the east, which is the conservatory. It is built with a span roof, and is glazed on the two sides and one end, the other end communicating with the house, from which it is entered through the parlor. . . .
- “The advantages are so many and important, of having the green-house connected with the mansion, either through the library or parlor, that we have often wondered at their generally isolated situation. This is particularly the case around Boston, where there is scarcely a green-house, certainly not one of any size or beauty, which connects with the living rooms to the dwelling house. We hope that those who are about erecting plant structures will bear this in mind. . . .
- “A green-house, strictly speaking, is but a place for the preservation of plants, and not for the growth of them; and the idea which some persons have, that all sorts and kinds may be grown in them is entirely erroneous.”
- Hovey, C. M., October 1841, “Notes made during a Visit to New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore, &c.,” describing the garden of T. Dunlap, Haerlem Plain, N.Y. (Magazine of Horticulture 7: 326)
- “The principal object of notice upon Mr. Dunlap’s place is the green-house, which is built on a somewhat novel plan. It is a span-roofed house, composed of glass, with the exception of a flat blank roof in the centre, about four feet wide, against the sides of which the glass abuts. The house is seventy-five feet long and twenty-five feet wide, and cost about twelve hundred dollars. The walls are built of brick, with a cavity between the outer and inner wall, for the circulation of air, and to act as a non-conductor. By this means, the cold is more effectually excluded, as bricks are a ready conductor of either heat or cold; and where back walls to houses are built of brick, we should always advise this. Mr. Dunlap’s green-house has no side-sashes. The novelty of the plan, however, is the stage, which is quite different from any thing we have ever seen. Wishing not to lose any heat, and having always observed the great quantity of waste room in a green-house, particularly under the stages, he thought of the expediency of building the latter of brick, and making the whole work solid. The experiment was tried, and so far it has proved a great economizer of fuel. The bricks are laid in Roman cement, and the work being well done, the stages are as smooth and level as if made of plank or boards, in the usual manner: there is consequently no lost room to be heated, and all that is given out by the flue is radiated throughout the house. So far as economy of fuel is the object, and for the purposes of the nurseryman, Mr. Dunlap’s plan is a very good one; but where neatness and lightness of the interior is a consideration, we should not advise a departure from the old mode. The house is warmed wholly with brick flues, running each side of the house, the stage being in the middle, between the walks.”
- Hovey, C. M., October 1841, “Notes made during a Visit to New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore, &c.,” describing the residence of J. Cox, New York, N.Y. (Magazine of Horticulture 7: 370)
- “Attached to the house is a kind of greenhouse or plant cabinet, in which a variety of plants are kept during winter; and, in the place of a larger structure, contributes much to the pleasure of the family.”
- Hovey, C. M., November 1841, “Notes made during a Visit to New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore, &c.,” describing the residence of James Dundas, Philadelphia, Pa. (Magazine of Horticulture 7: 420)
- “The garden is laid out with a large circular grass plat in the centre, about a hundred feet in diameter, and back of this, against the wall in the rear, is the green-house, a handsome building, about thirty feet long, and sixteen wide, corresponding in its architecture with the house.”
- Hovey, C. M., April 1842, “Notes made during a Visit to New York, Philadelphia, Baltimore, &c.,” describing the grounds of Robert Buist’s City Nursery and Greenhouse, Philadelphia, Pa. (Magazine of Horticulture 8: 124)
- “On it is a green-house, forty feet long; a camellia-house facing the north, forty feet; a hothouse, forty feet; and a geranium-house; about forty feet, the whole being a connected range. In addition to this, there is a rose-house, lately erected, about forty feet long. The whole we found well filled, for the season of the year, with a choice collection of healthy and well grown plants. The camellias were in excellent health; they are kept in the house the year round.”
- Notman, John, 26 December 1846, describing his designs for the Smithsonian Institution, Washington, D.C. (quoted in Greiff 1979: 119) [31]
- “No. 4 is the south front, and shews the elevation of the greenhouse and conservatory. I have not embodied those places in my design, but as applique, as they are unwholesome, their required surfaces of light does not agree with any style of architecture; but as adjunct, they require a great deal of dirty work and material in them, which is better done if they are out of direct observation The size of them is 30 feet by 65 feet each, and 25 feet high in the centre; they are directly entered from the building, and will be highly ornamental thus placed and formed, as a parallel perspective view of this front would shew.”
- Earle, Pliny, January 1848, describing the Bloomingdale Asylum for the Insane, New York, N.Y. (Journal of Medicine 10: 61)
- “The principle out-buildings on the premises are a barn, including stables and carriage-house, an ice-house, and a green-house, or conservatory. The barn is large, and built of stone in the most substantial manner. The green-house contains about seven hundred plants, many of them rare and beautiful exotics.”
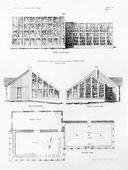
- Kirkbride, Thomas S., April 1848, describing the pleasure grounds and farm of the Pennsylvania Hospital for the Insane, Philadelphia, Pa. (American Journal of Insanity 4: 348)
- “East of the entrance is the private yard and residence of the Phy[sic]ian of the Institution, being the mansion house on the farm when purchased by the Hospital. The vegetable garden containing three and a half acres is next, and in it are the green-house, hot-beds, seed-houses, &c.”
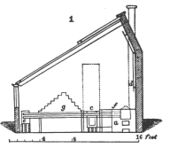
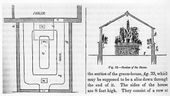
- Downing, A. J., 17 June 1848, in a letter to Cora L. Barton, describing Montgomery Place, country home of Mrs. Edward (Louise) Livingston, Dutchess County, N.Y. (quoted in Haley 1988: 34–35) [32]
- “I should be very glad to aid you in the plan ofyour pit—but perhaps shall need more definite details. What you describe is rather a small greenhouse than a pit. . . .
- “What, I imagine, you require, is a sort of propagating pit—and I would recommend one the form of which you will easily understand by the section which I send you on the next page.
- “This is a sort of cheap span-roof building part of which is glass & the other part, viz the roof towards the north shingled. Under this roof, which is just high enough to allow a person to walk upright, is the walk. The roof is supported by a line of posts, a, which rest on the back wall of the pit or stage. . . . In this country I do not find it of the least importance what the angle is for a house of this kind—there is so much sun & light.” [Fig. 12]
- Downing, A. J., 1851, describing plans for improving the public grounds in Washington, D.C. (quoted in Washburn 1967: 55) [33]
- “6th: The Botanic Garden
- “This is the spot already selected for this purpose and containing three green-houses. It will probably at some future time, be filled with a collection of hardy plants. I have only shown how the carriage-drive should pass through it (Crossing the canal again here) and making the exit by a large gateway opposite the middle gate of the Capitol Grounds.”
- Horticola [pseud.], March 1852, “Notes on Gardens and Country Seats Near Boston,” describing the residence of Timothy Bigelow, near Brighton, Mass. (Horticulturist 7: 127)
- “The residence of Mr. BIGELOW, near Brighton, is a prettily situated spot, nestling snugly on the sunny slope of a hill-side. There we found a pretty good range of hot-houses, consisting of two graperies, with a small green-house in the center; the latter rather small, badly contrived, but containing a nice assortment of green-house plants.”
Citations
- A.-J.[Dézallier d’Argenville, A.-J.], 1712, The Theory and Practice of Gardening ([1712] 1969: 75) [34]
- “GREEN-HOUSES are large Piles of Building like Galleries, which, by their Fronts, add to the Beauty of Gardens; besides that they are of
absolute Necessity to be built, for preserving Orange-Trees, and other Plants, in Cases, during the Winter.”
- Bradley, Richard, 1720, New Improvements of Planting and Gardening (2.3:198, 202, 204) <ref>Richard Bradley, New Improvements of Planting and Gardening, Both Philosophical and Practical; Explaining the Motion of the Sapp and Generation of Plants. With Other Discoveries Never before Made in Publick, for the Improvement of Forest-Trees, Flower-Gardens or Parterres; with a New Invention Where by More Designs of Garden Platts May Be Made in an Hour, than Can Be Found in All the Books Now Extant. Likewise Several Rare Secrets for the Improvement of Fruit-Trees, Kitchen-Gardens, and Green-House Plants., 3rd edn, 2 vols. (London: W. Mears, 1719)
- “The Green-Houses, as they are commonly built, serve more for Ornament than Use; their Situation to receive the South Sun, is the only thing that seems to be regarded towards the Health of the Plants they are to shelter: It is rare to find one among them that will keep a Plant well in the Winter, either by reason of their Situation in moist places, their want of Glasses enough in the Front, the Disproportion of the Room within them; and sometimes where it happens that a Green-House has been well consider’d in these Points, all is confounded by the Flues under it, which convey the Heat from the Stoves....
- “a good Green-House ought to be situated upon the driest Ground, to be as free from Damps as possible; . . . and yet upon occasion to let in Air freely, but chiefly to contrive that the Front of the House be so dispos’d, that nothing may obstruct the Passage of the Sun’s Rays in the Winter into the House. . . .
- “The Walls towards the North and the East must be of a good Thickness, but the Front towards the South should be all of Glass, excepting a low Wall about a Foot high from the Ground.”
Images
Inscribed
George Washington, Alternate plan (“Plan No. 1”) for the greenhouse at Mount Vernon, n.d.
George Washington, Alternate plan (“Plan No. 2”) for the greenhouse at Mount Vernon, n.d.
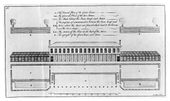
Batty Langley, “An Improvement of a beautiful Garden at Twickenham,", in New Principles of Gardening (1728), pl. IX.
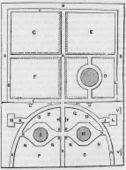
Philip Miller, “The Ground Plan of the Green house” and “The Ground Plan of the two Stoves,” in The Gardeners Dictionary ([1754] 1969), p. 577.
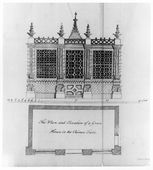
William Halfpenny, “The Plan and Elivation of a Green House in the Chinese Taste,” in Rural Architecture in the Chinese Taste (1755), pl. 42.
Samuel Vaughan, Plan of the buildings and grounds of Mount Vernon, 1787.
Andrew Craigie, Proposed Outbuildings for the Craigie Estate, December 11, 1791.
William Dandridge Peck, Plan of the botanic garden of Mr. Curtis, Newbury, Mass., Feb. 19, 1805.
Charles Willson Peale, Letter to Angelica Peale describing his garden at Belfield, November 22, 1815.
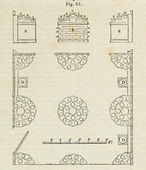
J. C. Loudon, Plan, view, and section of green-house, in An Encyclopaedia of Gardening (1826), p. 811, fig. 567.
J. C. Loudon, Greenhouse or conservatory for a flower-garden, with a span roof, in An Encyclopaedia of Gardening (1826), p. 811, fig. 568.
Joshua Barney, Map of the Hampton Estate, 1843.
George William Johnson, Floriculture Building, in A Dictionary of Modern Gardening (1847), p. 230, fig. 51.
Thomas S. Sinclair, "Plan of the Pleasure Grounds and Farm of the Pennsylvania Hospital for the Insane at Philadelphia," in Thomas S. Kirkbride, American Journal of Insanity 4 (April 1848): n.p.
A. J. Downing, Sketch of a “Propagating Pit” (or greenhouse) at Montgomery Place, June 17, 1848.
Anonymous, "Plan of a small Green-House" and "Section of the Same," in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 3, no. 6 (December 1848): figs. 32 and 33.
Anonymous, “Design for a Country House,” in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 4, no. 6 (December 1849): pl. opp. p. 249.
Anonymous, "A Country House in the Pointed Style," in A. J. Downing, The Architecture of Country Houses (1850), pl. opp. p. 304, figs. 133 and 134.
Frances Palmer, "Design for a Vinery & Green House," in William H. Ranlett, The Architect (1851), vol. 2, pl. 43.
Frances Palmer, "Cottage Villa in the Anglo Swiss Style," in William H. Ranlett, The Architect (1851), vol. 2, pl. 60, design 52.
Frances Palmer, "Cottage Villa in the earliest English Style," in William H. Ranlett, The Architect (1851), vol. 2, pl. 60, design 53.
Associated
Oscar Alexander Lawson, Robert Buist: Nurseryman & Florist, n.d.
Jeremiah Paul, “Robert Morris’ Seat on Schuylkill,” July 20, 1794.
Samuel McIntire, “South Front of the Green house in the East Building," Elias Hasket Derby House, n.d.
John Archibald Woodside, Lemon Hill, 1807.
William Russell Birch, "Woodlands, the Seat of Mr. Wm. Hamilton, Pennsylva.," 1808, in William Russell Birch and Emily Cooperman, The Country Seats of the United States (2009), p. 69, pl. 14.
Hugh Reinagle, Elgin Garden on Fifth Avenue, c. 1812.
Charles Willson Peale, View of the garden at Belfield, 1816.
Robert Squibb, Green-House: front and back walls, in The Gardener’s Calendar for the States of North Carolina, South Carolina, and Georgia (1827), frontispiece.
William Satchwell Leney, View of the Botanic Garden of the State of New York, 1828.
James E. Teschemacher, "A green-house constructed at the centre of a cottage," in Horticultural Register and Gardener's Magazine vol. 1 (May 1, 1835), opp. p. 157.
John Notman, “No. 1 Ground Plan, Smithsonian Institute,” December 23, 1846.
George William Johnson, Flower Pot, in A Dictionary of Modern Gardening (1847), p. 230, fig. 47.
George William Johnson, Flower Pot, in A Dictionary of Modern Gardening (1847), p. 230, fig. 48.
George William Johnson, Flower Pot, in A Dictionary of Modern Gardening (1847), p. 230, fig. 49.
George William Johnson, Flower Pot, in A Dictionary of Modern Gardening (1847), p. 230, fig. 50.
Anonymous, "Design for a Flower Garden," in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 2, no. 12 (June 1848): p. 558, fig. 67.
Anonymous, "Cottage Residence of Wm. H. Aspinwall, Esq.," in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), pl. opp. p. 51, fig. 8.
Anonymous, A Country House in the Pointed Style, in A. J. Downing, The Architecture of Country Houses (1850), pl. opp. p. 304, fig. 133.
Anonymous, “Rural Gothic Villa,” in A. J. Downing, The Architecture of Country Houses (1850), pl. opp. p. 322, fig. 148.
Attributed
John Izard Middleton, Greenhouse, 1813.
Nicolino Calyo, Harlem, the Country House of Dr. Edmondson, 1834.
Joseph Jacques Ramée, Estate plan for Calverton [detail], c. 1816, in Parcs & jardins (c. 1836), pl. 1.
Augustus Weidenbach, Belvedere, c. 1858.
Notes
- ↑ A disadvantage of cast iron technology was that condensation developed as a result of iron’s high thermal conductivity. Humidity control, always a concern, became a real issue in design. Therese O’Malley, Glasshouses: The Architecture of Light and Air (Bronx, N.Y.: The Garden, 2005) view on Zotero
- ↑ Michael F. Trostel, Mount Clare, Being an Account of the Seat Built by Charles Carroll, Barrister, upon His Lands at Patapsco (Baltimore: National Society of the Colonial Dames of America in the State of Maryland, 1981), 120, fn. 2 view on Zotero
- ↑ “Description of the Polmaise Mode of Heating Greenhouses,” Horticulturist 3 (September 1848): 122–27.
- ↑ John Bartram, The Correspondence of John Bartram, 1734-1777, ed. by Edmund Berkeley and Dorothy Smith Berkeley (Gainesville: University Press of Florida, 1992) view on Zotero
- ↑ Carmen Weber, "The Greenhouse Effect: Gender-Related Traditions in Eighteenth-Century Gardening," in Landscape Archaeology: Reading and Interpreting the American Historical Landscape, ed. by Rebecca Yamin and Karen Bescherer Metheny (Knoxville: The University of Tennesee Press, 1996), 32–51 view on Zotero
- ↑ Carl R. Lounsbury, ed., An Illustrated Glossary of Early Southern Architecture and Landscape (New York: Oxford University Press, 1994). View on Zotero
- ↑ Peter Martin, The Pleasure Gardens of Virginia: From Jamestown to Jefferson (Princeton, N.J.: Princeton University Press, 1991). View on Zotero
- ↑ William Darlington, Memorials of John Bartram and Humphry Marshall: With Notices of Their Botanical Contemporaries (Philadelphia: Lindsay & Blakiston, 1849). View on Zotero
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Barbara Wells Sarudy, "Eighteenth-Century Gardens of the Chesapeake," Journal of Garden History 9, no. 3 (July-September 1989), 104–59. View on Zotero
- ↑ Mary M. Ambler, "Diary of M. Ambler, 1770," Virginia Magazine of History and Biography 45, no. 2 (April 1937): 152–70. View on Zotero
- ↑ Gerald W. Johnson, Mount Vernon: The Story of a Shrine (New York: Random House, 1953). View on Zotero
- ↑ Michael Trostel, Mount Clare, Being an Account of the Seat Built by Charles Carroll, Barrister, upon His Lands at Patapsco (Baltimore: National Society of the Colonial Dames of America in the State of Maryland, 1981). View on Zotero
- ↑ Manasseh Cutler, Life, Journals and Correspondence of Rev. Manasseh Cutler, L.L.D., ed. by William Parker Cutler and Julia Perkin Cutler, 2 vols. (Cincinnati: Robert Clarke & Co., 1888). View on Zotero
- ↑ J.-P. (Jacques-Pierre) Brissot de Warville, New Travels in the United States Performed in 1788 (New York: T. & J. Swords, 1792). View on Zotero
- ↑ 15.0 15.1 15.2 Charles Arthur Hammond, "'Where the Arts and the Virtues Unite': Country Life Near Boston, 1637-1864" (unpublished Ph.D. diss., Boston University, 1982). View on Zotero
- ↑ Kenneth Roberts, and Anna M. Roberts, eds., Moreau de St. Méry’s American Journey, [1793-1798] (Garden City, N.Y.: Doubleday, 1947). View on Zotero
- ↑ "A Schedule of Property within the State of Pennsylvania Conveyed by Robert Morris, to the Hon. James Biddle, Esq. And Mr. William Bell, in Trust for the use and account of the Pennsylvania Property Company," c. September 6, 1797, Autograph Collection of the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, original MS reproduced Robbins, 1987, 136. View on Zotero
- ↑ Fiske Kimball, Mr. Samuel McIntire, Carver, the Architect of Salem (Portland, Maine: Southworth-Anthoensen, 1940). View on Zotero
- ↑ Masnasseh Cutler, Life, Journals and Correspondence of Rev. Manasseh Cutler, L.L.D., ed. by William Parker Cutler and Julia Perkin Cutler, 2 vols. (Cincinnati: Robert Clarke & Co, 1888). View on Zotero
- ↑ Alan Emmet, So Fine a Prospect: Historic New England Gardens (Hanover, N.H.: University Press of New England, 1996), View on Zotero
- ↑ David Hosack, Catalogue of Plants Contained in the Botanic Garden at Elgin (New York: T. and Y. Swords, 1806). View on Zotero
- ↑ Thomas Jefferson, The Garden Book, ed. by Edwin M. Betts (Philadelphia: American Philosophical Society, 1944). View on Zotero
- ↑ David Hosack, A Statement of Facts Relative to the Establishment and Progress of the Elgin Botanic Garden (New York: C. S. Van Winkle, 1811). View on Zotero
- ↑ Therese O’Malley, Therese, "Art and Science in American Landscape Architecture: The National Mall, Washington, D.C. 1791-1852" (Ph.D. dissertation, University of Pennsylvania, 1989). View on Zotero
- ↑ William Cullen Bryant, The Letters of William Cullen Bryant vol. 1, ed. by William Cullen II Bryant and Thomas G. Voss (New York: Fordham University Press, 1975). View on Zotero
- ↑ Lillian B. Miller, and et al, eds., The Selected Papers of Charles Willson Peale and His Family: Charles Willson Peale: Artist in Revolutionary America, 1735-1791. Vol. 1; Charles Willson Peale, Artist as Museum Keeper, 1791-1810. Vol 2, Pts. 1-2; The Belfield Farm Years, 1810-1820. Vol. 3; The Autobiography of Charles Willson Peale. Vol. 5. (New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Press, 1983–2000). View on Zotero
- ↑ James Boyd, A History of the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society, 1827-1927 (Philadelphia: Pennsylvania Horticultural Society, 1929). View on Zotero
- ↑ Martha Ogle Forman, Plantation Life at Rose Hill: The Diaries of Martha Ogle Forman, 1814-1845 (Wilmington, Del.: Historical Society of Delaware, 1976). View on Zotero
- ↑ Thaddeus William Harris, A Discourse Delivered before the Massachusetts Horticultural Society on the Celebration of Its Fourth Anniversary, October 3, 1832 (Cambridge, Mass.: E. W. Metcalf, 1832). View on Zotero
- ↑ Carmen Weber, "The Greenhouse Effect: Gender-Related Traditions in Eighteenth-Century Gardening," in Landscape Archaeology: Reading and Interpreting the American Historical Landscape, ed. by Rebecca Yamin and Karen Bescherer Metheny (Knoxville: The University of Tennesee Press, 1996), pp. 32–51. View on Zotero
- ↑ Constance Greiff, John Notman, Architect, 1810-1865 (Philadelphia: Athenaeum of Philadelphia, 1979). View on Zotero
- ↑ Jacquetta M. Haley, ed., Pleasure Grounds: Andrew Jackson Downing and Montgomery Place (Tarrytown, N.Y.: Sleepy Hollow Press, 1988). View on Zotero
- ↑ Wilcomb E. Washburn, "Vision of Life for the Mall," AIA Journal, 47, no. 3 (March 1967): 52–59. View on Zotero
- ↑ A.-J. (Antoine Joseph) Dézallier d’Argenville, The Theory and Practice of Gardening; Wherein Is Fully Handled All That Relates to Fine Gardens, ... Containing Divers Plans, and General Dispositions of Gardens; ..., trans. by John James (London: Geo. James, 1712). View on Zotero