Difference between revisions of "Vase/Urn"
A-whitlock (talk | contribs) |
|||
| (90 intermediate revisions by 10 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| + | [[File:1175.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 1, Anonymous, “A fine terra-cotta vase,” [[A. J. Downing]], “Remarks on the Different Styles of Architecture,” ''American Gardeners’ Magazine'' vol. 2, no. 8 (August 1836): 286, fig. 11.]] | ||
| − | The term vase typically referred to a freestanding, symmetrical vessel having a wider mouth than foot [Fig. 1], although some British pattern books included types with narrow mouths and elaborate lids [Fig. 2]. If fitted with a foot or pedestal set on either a small base or plinth, the vessel sometimes was referred to as an urn. Throughout history, ashes of the dead have been deposited in urns, giving them symbolic importance. Frequently urns were used for memorials and monuments, especially in cemeteries | + | [[File:1728.jpg|thumb|Fig. 2, [[James Gibbs]], Nine of “Fifty four Draughts of Vases,” in ''A Book of Architecture'' (1728), pl. 139.]] |
| + | [[File:1840.jpg|thumb|Fig. 3, [[J. C. Loudon]], “Garden Front of Cheshunt Cottage,” in ''The Gardener's Magazine'' 15, no. 117 (December 1839): 669, fig. 174.]] | ||
| + | [[File:0251.jpg|thumb|Fig. 4, Charles Codman, ''Kalorama'', 1821.]] | ||
| + | The term vase typically referred to a freestanding, symmetrical vessel having a wider mouth than foot [Fig. 1], although some British pattern books included types with narrow mouths and elaborate lids [Fig. 2]. If fitted with a foot or pedestal set on either a small base or plinth, the vessel sometimes was referred to as an urn. Throughout history, ashes of the dead have been deposited in urns, giving them symbolic importance. Frequently urns were used for memorials and monuments, especially in [[cemetery|cemeteries]]. In the context of the designed landscape, treatise writers often strongly recommended that the vase be placed on top of a pedestal or plinth so that it would be easily visible. [[Andrew Jackson Downing|A. J. Downing]] elaborated upon this point in an 1836 article about architecture and at greater length in his 1849 treatise, when he explained that without such a placement, the vase would appear as a temporary, accidental introduction to the landscape. A permanent base, in his opinion, gave the vase the “character of art, at once more dignified and expressive of stability” [Fig. 3]. | ||
| − | Vases functioned primarily as ornamentation and were associated with a number of garden features. In his eighteenth-century treatise, | + | Vases functioned primarily as ornamentation and were associated with a number of garden features. In his eighteenth-century treatise, Antoine-Joseph Dezallier d’Argenville suggested that vases could be used to decorate [[parterre]]s, placed amidst planting features (such as [[grove]]s) or in water features (such as [[basin]]s), situated at the termination of [[walk]]s and [[vista]]s, or housed within structures (such as [[portico]]s and [[arbor]]s). |
| − | Vases continued to be featured in ornamental landscapes well into the | + | Vases continued to be featured in ornamental landscapes well into the 19th century, despite many changes in garden design. A painting of Kalorama, for example, depicts a vase at the center of the [[view]] [Fig. 4]. The connection between vases and water features continued as well. [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing’s]] texts, for example, contain numerous references to vases as [[fountain]]s. The strategic placement of vases in [[pleasure ground]]s also endured. At the early 19th-century estate of [[Blithewood]] in Dutchess County, New York, vases of grey Maltese stone (which [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] praised for its ability to harmonize with vegetation) were used throughout the [[pleasure ground]]s and, in particular, at the corners of adjoining [[walk]]s. Vases were also used at the termination of [[walk]]s, where they served as visual focal points as in a suburban garden design described in 1848 in the ''Horticulturist''. |
| − | Treatise authors from different periods agreed that the vase should never be placed far from the house. Thomas Whately, in his 1770 treatise, insisted that the vase | + | Treatise authors from different periods agreed that the vase should never be placed far from the house. Thomas Whately, in his 1770 treatise, insisted that the vase “attend the mansion, and trespass a little upon the garden.” In 1849 [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] reiterated Whately's idea, explaining that since the vase was a “highly artificial and architectural” object, it must be situated in the [[pleasure ground]] in such a manner that it would always “appear in some way connected with buildings, or objects of a like architectural character.” He cautioned further that vases be used judiciously. If placed “indiscriminately. . . where they have really no place, but interfere with the quiet character of surrounding nature,” vases ran the danger of destroying the “unity of expression” that [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] and others sought. |
| − | The function and placement of the vase was closely connected to its style and form. As several treatise writers counseled, vases should be stylistically consistent with their settings and, when placed near the house, should reflect the architectural character of the structure, such as Gothic, Grecian, Roman, or Italianate styles. In nineteenth-century treatises, vases in the classical or ancient style emerged as the most popular. A favored model was the Warwick Vase, a carved and decorated white marble vase from Hadrian’s Villa. The vase was recovered from the Roman site in 1770 by the Englishman William Hamilton and was subsequently taken to England by his nephew, George, Earl of Warwick. At Montgomery Place, designed by Alexander Jackson Davis and Downing in the 1840s, a Warwick-style vase was placed in the center of the flower garden [Fig. | + | [[File:0852.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 5, [[Alexander Jackson Davis]], “The [[Conservatory]],” [[Montgomery Place]], c. 1839.]] |
| + | The function and placement of the vase was closely connected to its style and form. As several treatise writers counseled, vases should be stylistically consistent with their settings and, when placed near the house, should reflect the architectural character of the structure, such as Gothic, Grecian, Roman, or Italianate styles. In nineteenth-century treatises, vases in the classical or [[ancient style]] emerged as the most popular. A favored model was the Warwick Vase, a carved and decorated white marble vase from Hadrian’s Villa. The vase was recovered from the Roman site in 1770 by the Englishman [[William Hamilton]] and was subsequently taken to England by his nephew, George, Earl of Warwick. At [[Montgomery Place]], designed by [[Alexander Jackson Davis]] and [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] in the 1840s, a Warwick-style vase was placed in the center of the flower garden [Fig. 5]. In 1849, [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] described the popular option of the [[Rustic_style|rustic-style]] vase, in which the vessel was made out of the “branches and sections of trees with the bark attached.” | ||
| − | Outdoor vases were usually large in scale, two to three feet in height. They could be composed of a variety of materials, such as cast-brass, lead gilt, marble, stone and stucco, according to | + | [[File:0218.jpg|thumb|Fig. 6, Augustus Weidenbach, ''[[Belvedere]]'', c. 1858.]] |
| + | Outdoor vases were usually large in scale, two to three feet in height. They could be composed of a variety of materials, such as cast-brass, lead gilt, marble, stone and stucco, according to Dezallier d’Argenville. [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]], writing nearly one hundred and fifty years later, gave an equally wide-ranging list, including stone, artificial stone, plaster, and Roman cement. He also cited inexpensive materials intended to imitate luxury materials, such as terra-cotta and English Staffordshire, which could be treated to emulate marble. [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing's]] allusion to Staffordshire pottery suggests the near-dominant presence of refined British pottery in America. Nevertheless, he mentioned several American manufacturers that produced vases and noted especially such New York manufacturers as the Salamander Works, the Garnick Company, and Coffee’s Manufactory. | ||
| − | Vases were also used as plant containers, as indicated in Augustus Weidenbach’s c. 1858 painting of the garden at Belvedere in Baltimore [Fig. | + | Vases were also used as plant containers, as indicated in Augustus Weidenbach’s c. 1858 painting of the garden at [[Belvedere]] in Baltimore [Fig. 6], or in C. M. Hovey's 1839 description of a greenhouse or conservatory. Nevertheless, large-scale, ornamental vases were often regarded as works of art, and, therefore, as [[J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon|J. C. Loudon]] argued, cited by [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] in 1849, they should not be reduced to the level of “a mere garden flower-[[pot]].” |
| − | + | —''Anne L. Helmreich'' | |
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
==Texts== | ==Texts== | ||
| + | ===Usage=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:1190.jpg|thumb|Fig. 7, Samuel McIntire, ''South Front of the [[Greenhouse|Green house]] in the East Building'', Elias Hasket Derby House, c. 1799.]] | ||
| + | * McIntire, Samuel, June 8, 1795, describing a statement of account with Elias Hasket Derby (quoted in Kimball 1940: 74)<ref>Fiske Kimball, ''Mr. Samuel McIntire, Carver, the Architect of Salem'' (Portland, ME: Southworth-Anthoensen, 1940), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/I9J3RBHB view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :{| | ||
| + | |“1793 ''Dec 4th'' || to Sundrie Drawings for <br /> [[Summer House]]s @ 24/ || £1: 4: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |1794 ''Apl 25'' || to Carving 4 '''Vases''' for <br /> the [[Summer House]] at 18/s each || 3: 18: | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |July || to Building the Summer <br /> House at the Farm @ 100:0:0 <br />to Extra work on the Same, <br />Viz., finishing four Closets <br />@20/each 4: 0:0” [Fig. 7] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * Ingraham, Joseph Holt, 1835, describing a [[plantation]] near New Orleans, LA (1:243)<ref>Joseph Holt Ingraham, ''The South-West'', 2 vols. (New York: Harper, 1835), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/DTFA8CCM view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| − | + | : “Passing from this [[plantation]] scene through the airy hall of the dwelling, which opened from [[piazza]] to [[piazza]] through the house, to the front gallery, whose light columns were wreathed with the delicately leaved Cape-jasmine, rambling woodbine and honeysuckle, a lovelier and more agreeable scene met my eye. I stood almost embowered in the foliage of exotics and native plants, which stood upon the gallery in handsome '''vases''' of marble and China-ware. The main avenue opened a [[vista]] to the river through a paradise of althea, orange, lemon, and olive trees, and [[grove]]s and [[lawn]]s extended on both sides of this lovely spot, ‘Where Flora’s brightest broidery shone,’ terminating at the villas of adjoining [[plantation]]s.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:1118.jpg|thumb|Fig. 8, W. H. Bartlett, "Undercliff Near Cold-Spring. (The Seat of General George P. Morris)," in Nathaniel Parker Willis, ''American Scenery; or, Land, Lake and River Illustrations of Transatlantic Nature'' (1840), vol. 2, pl. 11.]] | |
| − | + | * Willis, Nathaniel Parker, 1840, describing Undercliff, [[seat]] of General George P. Morris, near Cold-Spring, NY (1840; repr. 1971: 233)<ref>Nathaniel Parker Willis, ''American Scenery; Or, Land, Lake and River Illustrations of Transatlantic Nature'' (London: G. Virtue, 1840), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/FB4EQ56M view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [ | ||
| − | + | : “In front, a circle of greensward is refreshed by a [[fountain]] in the centre, gushing from a Grecian '''vase''', and encircled by ornamental [[shrubbery]]; from thence a gravelled [[walk]] winds down a gentle declivity to a second plateau, and again descends to the entrance of the carriage road, which leads upwards along the left [[slope]] of the hill, through a noble forest, the growth of many years, until suddenly emerging from its sombre shades, the visitor beholds the mansion before him in the bright blaze of day.” [Fig. 8] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Hovey, C. M. (Charles Mason), November 1841, describing Highland Place, estate of [[Andrew Jackson Downing|A. J. Downing]], Newburgh, NY (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 7: 405)<ref>Charles Mason Hovey, “Select Villa Residences, with Descriptive Notices of Each; Accompanied with Remarks and Observations on the Principles and Practice of Landscape Gardening: Intended with a View to Illustrate the Art of Laying Out, Arranging, and Forming Gardens and Ornamental Grounds,” ''Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs'' 7, no. 11 (November 1841): 401–11, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/SXS8ZS3J view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | : “7. Large palms in [[pot]]s, or Maltese '''vases''', or '''vases''' made of artificial stone, set on the turf. In the introduction of '''vases''', it should always be remembered that the '''vase''' should not be set down immediately on the turf, but upon a ''plinth''. . . | |
| − | + | : “8. [[Rustic_style|Rustic]] basket, for flowers, as represented in the engraving just referred to. These are very easily made. Mr. [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing]] has given a figure of one, in his ''Treatise on Landscape Gardening'', where he states they may be made in the following manner:—An octagon box serves as the body or frame of the '''vase'''; on this, pieces of birch and hazel, (small split limbs, covered with the bark,) are nailed closely, so as to form a sort of mosaic covering to the whole exterior.” | |
| − | vase, | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], October 1847, describing [[Montgomery Place]], country home of Mrs. Edward (Louise) Livingston, Dutchess County, NY (quoted in Haley 1988: 52)<ref>Jacquetta M. Haley, ed., ''Pleasure Grounds: Andrew Jackson Downing and Montgomery Place'' (Tarrytown, NY: Sleepy Hollow Press, 1988), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/SSZXJFSC view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | : “Passing under neat and tasteful [[Arch|archways]] of wirework, covered with rare climbers, we enter what is properly | |
| − | + | : “THE [[flower garden|FLOWER GARDEN]]. | |
| − | + | : “In the centre of the garden stands a large '''vase''' of the Warwick pattern; others occupy the centres of [[parterre]]s in the midst of its two main divisions, and at either end is a fanciful light [[summer house|summer-house]], or [[pavilion]], of Moresque character.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | of the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:0350.jpg|thumb|Fig. 9, [[Alexander Jackson Davis]], "[[View]] in the Grounds at [[Blithewood]]," in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), frontispiece.]] | |
| − | + | * [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], 1849, describing [[Blithewood]], [[seat]] of Robert Donaldson, Dutchess County, NY (1849; repr., 1991: 425)<ref name="Downing 1849"> A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America'', 4th ed. (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/K7BRCDC5 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | : “At [[Blithewood]], the seat of R. Donaldson, Esq., on the Hudson, a number of exquisite '''vases''' may be seen in the [[pleasure ground|pleasure-ground]]s, which are cut in Maltese stone. These were imported by the proprietor, direct from Malta, at very moderate rates, and are not only ornamental, but very durable. Their color is a warm shade of grey which harmonizes agreeably with the surrounding vegetation.” [Fig. 9] | |
| − | |||
| − | of the | ||
| − | |||
| − | and | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | * Twain, Mark, October 26, 1853, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (quoted in Gibson 1988: 2)<ref>Jane Mork Gibson, “The Fairmount Waterworks,” ''Bulletin, Philadelphia Museum of Art'' 84 (1988): 5–40, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/RZEZDDEN view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | : “We arrived at Fairmount. . . Seeing a park at the foot of the hill, I entered—and found it one of the nicest little places about. Fat marble Cupids, in big marble '''vases''', squirted water upward incessantly.” | |
| − | + | {{break}} | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Citations=== | ===Citations=== | ||
| − | + | * Dézallier d’Argenville, Antoine-Joseph, 1712, ''The Theory and Practice of Gardening'' (1712; repr., 1969: 75–76)<ref>A.-J. (Antoine Joseph) Dézallier d’Argenville, ''The Theory and Practice of Gardening; Wherein Is Fully Handled All That Relates to Fine Gardens, . . . Containing Divers Plans, and General Dispositions of Gardens; . . . ,'' trans. by John James (London: Geo. James, 1712), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/RNT8ZVZ8 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | and Practice of Gardening ([ | + | |
| + | : “STATUES and '''Vases''' contribute very much to the Embellishment and Magnificence of a Garden, and extremely advance the natural Beauties of it. They are made of several Forms, and different Materials; the richest are those of Cast-Brass, Lead gilt, and Marble; the ordinary Sort are of common Stone, or Stucco. . . | ||
| + | : “THE usual Places of Figures and '''Vases''' are along the Palisades, in the Front, and upon the Sides of a [[parterre|Parterre]]; in the Niches and Sinkings of Horn-beam, or of Lattice-work made for that Purpose. In [[grove|Grove]]s, they are placed in the Center of a Star, or S. ''Andrew’s'' Cross; in the Spaces between the [[walk|Walk]]s of a Goose-foot, in the Middle of Halls and Cabinets, among the Trees and [[arch|Arch]]es of a Green-Gallery, and at the Head of a Row of Trees, or Palisades, that stand free and detached. They are also put at the lower End of [[walk|Walk]]s and [[vista|Vista]]s, to set them off the better; in [[portico|Portico]]s, and [[arbor|Arbor]]s of [[trellis|Trellis]]-work; in [[basin|Bason]]s, [[cascade|Cascade]]s, &c. In general, they do well every where; and you can scarce have too many of them in a Garden: But, as in the Business of Sculpture, it should be excellent, as well as in Painting and Poesy [''sic''] (which are its two Sisters).” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:1727.jpg|thumb|Fig. 10, [[James Gibbs]], “Three Designs for Vases,” in ''A Book of Architecture'' (1728), pl. 138.]] | ||
| + | * [[Gibbs, James]], 1728, ''A Book of Architecture'' (1728: xxi, xxv)<ref>James Gibbs, ''A Book of Architecture, Containing Designs of Buildings and Ornaments'' (London: Printed for W. Innys et al., 1728), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/ZGUVPFG8 view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “Three Designs for Columns, proper for publick Places or private Gardens; ''viz''. a plain Dorick [[column|Column]] upon its Pedestal with a '''Vase''' a top, a fluted [[column|Column]] properly adorn’d, and a [[Rustic_style|Rustick]] frosted [[column|Column]], with a Figure a-top, as I have made them for several Gentlemen. The Proportions of them are mark’d upon an upright Line, divided into so many Diameters of the [[column|Column]] for the Height. . . | ||
| + | : “Three Designs for '''Vases''', done for the Right Honourable the Earl of ''Oxford''. There are two '''Vases''' well executed in Portland Stone according to the middle Draught, which are set upon two large Peers on each side of the principal [[walk|Walk]] in the Garden at ''Wimpole'' in ''Cambridgeshire''. . . [Fig. 10] | ||
| + | : “Fifty four Draughts of '''Vases''', &c. in the Antique manner, made for several persons at different times. Many of them have been executed both in Marble and Metal.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Whately, Thomas, 1770, ''Observations on Modern Gardening'' (1770; repr., 1982: 138)<ref>Thomas Whately, ''Observations on Modern Gardening'', 3rd ed. (London: Garland, 1982), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/QKRK8DCD view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “'''vases''', [[statue]]s, and termini, are usual appendages to a considerable edifice; as such they may attend the mansion, and trespass a little upon the garden, provided they are not carried so far into it as to lose their connection with the structure.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Noah Webster|Webster, Noah]], 1828, ''An American Dictionary of the English Language'' (1828: n.p.)<ref>Noah Webster, ''An American Dictionary of the English Language'', 2 vols. (New York: S. Converse, 1828), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/N7BSU467 view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “'''URN'''. . . A kind of vase of a roundish form, largest in the middle; used as an ornament. ''Cyc''. . . | ||
| + | : “'''VASE''', ''n''. [Fr. from L. ''vas'', ''vasa'', a vessel; It. ''vaso''.] | ||
| + | : “1. A vessel for domestic use, or for use in [[temple]]s; as a '''''vase''''' for sacrifice, an '''urn''', &c. | ||
| + | : “2. An ancient vessel dug out of the ground or from rubbish, and kept as a curiosity. | ||
| + | : “3. In ''architecture'', an ornament of sculpture, placed on socles or pedestals, representing the vessels of the ancients, as incense-[[pot]]s, flower-[[pot]]s, &c. They usually crown or finish facades or frontispieces. ''Cyc''. | ||
| + | : “4. The body of the Corinthian and Composite capital; called also the tambor or drum.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], August 1836, “Remarks on the Fitness of the different Styles of Architecture for the Construction of Country Residences, and on the Employment of Vases in Garden Scenery” (''American Gardeners’ Magazine'' 2: 285–86)<ref>A. J. Downing, “Remarks on the Fitness of the different Styles of Architecture for the Construction of Country Residences, and on the Employment of Vases in Garden Scenery,” ''American Gardeners’ Magazine, and Register of Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Horticulture and Rural Affairs'' 2, no. 8 (August 1836): 281–86, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/keywords_in_early_american_landscape_design/items/itemKey/J5HZKZAG view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “It will not be inadvertent to the present hasty remarks to hint at the additional charm which may be produced in highly finished places, especially where the buildings are in the Grecian style, by introducing into the [[lawn]]s and gardens the classic '''''vase''''' in its different forms, and, if thought desirable, [[statue]]s also. They serve as it were as a connecting link between so highly artificial an object as a modern villa, and the verdant [[lawn]]s and gay gardens which surround it. Elevated upon pedestals, and placed at suitable points in the [[view]]—on the parapets of [[terrace]]s near the house—before a group of foliage upon the [[lawn]], and at proper intervals in the garden, they give a classic and elegant air to the whole, which adds greatly to its value. Beautiful in their forms, contrasting finely with the deep green of vegetation, and leading the eye gradually from their own sculptured beauty to the architectural symmetry of the building, of which they form as it were a continuous though detached part, amalgamating it with the grounds in which it is placed—their effect can only be appreciated beforehand by those who have studied the excellent effect produced by their introduction into the scene. | ||
| + | : “Another reason which may be offered for the introduction of '''vases''' into architectural and garden scenery is ‘the gratification which such objects afford to the man of intelligence and taste. There are, perhaps, few objects, next to the human figure, which afford as many interesting historical associations as the '''vase'''. It may truly be said to be the first and last production of the plastic art. The first utensil formed by man, in the dawn of civilization in every country, is a vessel or '''vase''' for holding water; and that on which the highest resources of art are bestowed, in ages of the greatest refinement, is a '''vase''' or vessel for holding wine. In the first case, it is hollowed out of a gourd, or rudely shaped of clay, and dried in the sun; and, in the latter case, it is manufactured of costly metals or precious stones; or, if of common materials, such as stone, earthenware or glass, it is rendered valuable by the taste and skill bestowed on its form and ornaments. The history of every country may be traced by its '''vases''' no less than by its coins; and the history of all countries is set before us in the '''vases''' of all countries.’ [Loudon, X. 494.]” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *Hovey, C. M. (Charles Mason), January 1839, “Notes on Gardens and Nurseries” (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 5: 29)<ref>Charles Mason Hovey, “Notes on Gardens and Nurseries,” ''Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs'' 5, no. 1 (January 1839): 59–65, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/EQ6ZIWR4 view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “The beauty of '''vases''' in garden scenery has been already urged by our correspondent, Mr. [[A.J. Downing|Downing]], (Vol. II, p. 281,) and we had intended to add something to his remarks, ourselves, by the way of impressing the subject more upon the attention of our readers. . . | ||
| + | : “Surely we need not say any thing further to show how much they would add to the beauty of the garden, or the elegance of the [[conservatory]]. In either place, they are objects too inviting not to be found in every garden. These '''vases''' are easily filled with handsome plants, well suited to the situation, and the following might compose, in part, the group for the [[greenhouse|green-house]].” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * Rusticus [pseud.], August 1846, “Design for a Rustic Gate” (''Horticulturist'' 1: 72)<ref>Rusticus [pseud.], “Design for a Rustic Gate,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 1, no. 2 (August 1846): 72–73, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/DPX658P3 view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “Indeed, [[Rustic_style|rustic work]] of all kinds is extremely pleasing in any situation where there is any thing like a wild or natural character; or even where there is a simple and [[Rustic_style|rustic character]]. In the immediate proximity of a highly finished villa, it strikes me that [[Rustic_style|rustic work]], such as [[arbor]]s, [[fence]]s, flower baskets and the like, are rather out of place. The sculptured '''vase''' of marble, or terra cotta, would appear to be the most in keeping with an elegant place of the first class; that is to say, for all situations very near the house. In wooded [[walk]]s, or secluded spots, [[Rustic_style|rustic]] work looks well always.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | * [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], July 1848, “Ornamental Vases and Chimney Tops” (''Horticulturist'' 3: 40)<ref>A. J. Downing, “Ornamental Vases and Chimney Tops,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 3, no. 1 (July 1848): 37–43, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/keywords_in_early_american_landscape_design/items/itemKey/5GK4MF9V view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “There are few objects that may, with so much good effect, be introduced into the scenery of [[pleasure ground]]s, surrounding a tasteful villa, as the '''''vase''''', in its many varied forms. The terra cotta '''vases''' of the Garnkirk company exhibit pleasing forms, and a soft mellow shade of colour, which harmonizes admirably with the hue of foliage and turf. From among the variety manufactured by them, we have selected a few, of which we here present engravings. . . | ||
| + | : “To set down a '''vase''' upon the earth, or the [[lawn]], without any pedestal, is to give it a temporary character, and to rob it of that dignity and importance which it gains, both to the eye and the reason, by being placed on a firm and secure pedestal. . . | ||
| + | : “Looking at the '''vase''' in an artistical point of view, it is considered as performing the office of uniting the architecture and the grounds of a complete country residence. It is the architectural idea, carried a little beyond the house, and shows that the same feeling of taste and embellishment reigns in both departments of the residence. It will be easily understood from this, that the most suitable place for '''vases''' is in highly kept portions of the [[pleasure ground]], near the house, where the '''vases''' may be seen in connexion with it; or, at least, where the architecture of the building harmonizes with the highly artificial forms of the '''vase'''. The simplest cottage may have its '''vase'''; but, where the building is small, the [[Rustic_style|rustic]] '''vase''', made of bits of wood, and filled with flowering plants, is in better keeping than those made of any more highly artificial materials.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:1819.jpg|thumb|Fig. 11, Anonymous, "A Gothic vase," in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 424, fig. 69.]] | ||
| + | * [[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], 1849, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849: 423–27, 471, 473)<ref name="Downing 1849"></ref> | ||
| + | |||
| + | : “Where there is a [[terrace]] ornamented with '''urns''' or '''vases''', and the proprietor wishes to give a corresponding air of elegance to his grounds, '''vases''', [[sundial]]s, etc., may be placed in various appropriate situations, not only in the architectural [[flower garden|flower-garden]], but on the [[lawn]], and through the [[pleasure ground|pleasure-ground]]s in various different points ''near the house''. We say near the house, because we think so highly artificial and architectural an object as a sculptured '''vase''', is never correctly introduced unless it appear in some way connected with buildings, or objects of a like architectural character. To place a beautiful '''vase''' in a distant part of the grounds, where there is no direct allusion to art, and where it is accompanied only by natural objects, as the overhanging trees and the sloping turf, is in a measure doing violence to our reason or taste, by bringing two objects so strongly contrasted, in direct union. But when we see a statue or a '''vase''' placed in any part of the grounds where a near [[view]] is obtained of the house (and its accompanying statues or '''vases'''), the whole is accounted for, and we feel the distant '''vase''' to be only part of, or rather a repetition of the same idea,—in other words, that it forms part of a whole, harmonious and consistent. | ||
| + | : “'''Vases''' of real stone, as marble or granite, are decorations of too costly a kind ever to come into general use among us. '''Vases''', however, of equally beautiful forms, are manufactured of artificial stone, of fine pottery, or of cast iron, which have the same effect, and are of nearly equal durability, as garden decorations. | ||
| + | : “A '''vase''' should never, in the open air, be set down upon the ground or grass, without being placed upon a firm base of some description, either a ''plinth'' or a ''pedestal''. Without a base of this kind it has a temporary look, as if it had been left there by mere accident, and without any intention of permanence. Placing it upon a pedestal, or square plinth (block of stone), gives it a character of art, at once more dignified and expressive of stability. Besides this, the pedestal in reality serves to preserve the vase in a perpendicular position, as well as to expose it fairly to the eye, which could not be the case were it put down, without any preparation, on the bare turf or gravel. | ||
| + | : “Figure 69 is. . . Gothic. . . These with many other elegant '''vases''' and '''urns''' are manufactured in an artificial stone, as durable as marble, by Austin of London, and together with a great variety of other beautiful sculpturesque decorations, may be imported at very reasonable prices. . . [Fig. 11] | ||
| + | : “These '''vases''', when colored to imitate marble or other stone, are extremely durable and very ornamental. As yet, we are unable to refer our readers to any manufactory here, where these articles are made in a manner fully equal to the English; but we are satisfied, it is only necessary that the taste for such articles should increase, and the consequent demand, to induce our artisans to produce them of equal beauty and of greater cheapness. . . | ||
| + | : “Large '''vases''' are sometimes filled with earth and planted with choice flowering plants, and the effect of the blossoms and green leaves growing out of these handsome receptacles, is at least unique and striking [[J. C. Loudon|Loudon]] objects to it in the case of an elegant sculptured '''vase''', ‘because it is reducing a work of art to the level of a mere garden flower-[[pot]], and dividing the attention between the beauty of the form of the '''vase''' and of its sculptured ornaments, and that of the plant which it contains.’ This criticism is a just one in its general application, especially when '''vases''' are considered as architectural decorations. Occasional deviations, however, may be permitted, for the sake of producing variety, especially in the case of vases used as decorations in the [[flower-garden]]. | ||
| + | [[File:0389.jpg|thumb|Fig. 12, Anonymous, “A pleasing [[Rustic_style|rustic]] vase”" in [[Andrew Jackson Downing|A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), p. 526, fig. 74.]] | ||
| + | : “A very pretty and fanciful substitute for the sculptured '''vase''', and which may take its place in the [[picturesque]] landscape, may be found in '''vases''' or baskets of ''rustic work'', constructed of the branches and sections of trees with the bark attached. Figure 74 is a representation of a pleasing [[Rustic_style|rustic]] '''vase''' which we have constructed without difficulty. A tripod of branches of trees forms the pedestal. An octagonal box serves as the body or frame of the '''vase'''; on this, pieces of birch and hazel (small split limbs covered with the bark) are nailed closely, so as to form a sort of mosaic covering to the whole exterior. Ornaments of this kind, which may be made by the amateur with the assistance of a common carpenter, are very suitable for the decoration of the grounds and [[flower garden|flower-garden]]s of cottages or [[picturesque]] villas. An endless variety of forms will occur to an ingenious artist in [[Rustic_style|rustic work]], which he may call in to the embellishment of rural scenes, without taxing his purse heavily. . . [Fig. 12] | ||
| + | [[File:0403.jpg|thumb|Fig. 13, Anonymous, “Tazza [[Fountain]],” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 471, fig. 93.]] | ||
| + | : “Weeping, or ''Tazza [[fountain|Fountain]]s'', as they are called, are simple and highly pleasing objects, which require only a very moderate supply of water compared with that demanded by a constant and powerful [[jet]]. The conduit pipe rises through and fills the '''vase''', which is so formed as to overflow round its entire margin. Figure 93 represents a beautiful Grecian '''vase''' for tazza [[fountain]]s. The ordinary [[jet]] and the tazza [[fountain]] may be combined in one, when the supply of water is sufficient, by carrying the conduit pipe to the level of the top of the '''vase''', from which the water rises perpendicularly, then falls back into the '''vase''' and overflows as before. . . [Fig. 13] | ||
| + | : “''Unity of expression'' is the maxim and guide in this department of the art, as in every other. Decorations can never be introduced with good effect, when they are at variance with the character of surrounding objects. A beautiful and highly architectural villa may, with the greatest propriety, receive the decorative accompaniments of elegant '''vases''', [[sundial]]s, or [[statue]]s, should the proprietor choose to display his wealth and taste in this manner; but these decorations would be totally misapplied in the case of a plain square edifice, evincing no architectural style in itself. | ||
| + | : “In addition to this, there is great danger that a mere lover of fine '''vases''' may run into the error of assembling these objects indiscriminately in different parts of his grounds, where they have really no place, but interfere with the quiet character of surrounding nature. He may overload the grounds with an unmeaning distribution of sculpturesque or artificial forms, instead of working up those parts where art predominates in such a manner, by means of appropriate decorations, as to heighten by contrast the beauty of the whole adjacent landscape.” | ||
| + | |||
| + | <hr> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Images== | ||
| + | ===Inscribed=== | ||
| + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:1727.jpg|[[James Gibbs]], “Three Designs for '''Vases''',” in ''A Book of Architecture'' (1728), pl. 138. | ||
| + | |||
| + | File:1728.jpg|[[James Gibbs]], Nine of “Fifty four Draughts of '''Vases''',” in ''A Book of Architecture'' (1728), pl. 139. | ||
| − | + | File:1190.jpg|Samuel McIntire, ''South Front of the [[Greenhouse|Green house]] in the East Building'', Elias Hasket Derby House, c. 1799. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1293_large.jpg|Asher Benjamin, “Designs for '''Urns''',” in ''The Architect, or Practical House Carpenter'' [(1830) 1972], 64, pl. 26. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1758.jpg|[[J. C. Loudon]], “[[Rustic_style|Rustic]] [[arch]] and '''vase''',” in ''The Suburban Gardener'' (1838), 581, fig. 231. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1827.jpg|[[J. C. Loudon]], “Hermit's [[Seat]], and Classical '''Vase''',” Cheshunt Cottage, in ''The Gardener's Magazine'' 15, no. 117 (December 1839): 664, fig. 172. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0878.jpg|Anonymous, “Ground Plan of a portion of Downing's [[Botanic_garden|Botanic Gardens]] and [[Nursery|Nurseries]],” in ''Magazine of Horticulture'' 7, no. 11 (November 1841): 404. "7. Large palms in '''pots''', or Maltese '''vases''', or '''vases''' made of artificial stone, set on the turf (. . .) 8. [[Rustic_style|Rustic]] basket, for flowers. . ." | |
| − | + | File:0941.jpg|Anonymous, “A pair of ''tozza'' [''sic''] '''vases''', for a [[fountain]],” in [[A. J. Downing]], ed., ''Horticulturist'' 3, no. 1 (July 1848): 42, fig. 13. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | [ | ||
| − | + | File:0948.jpg|Anonymous, Ornamental '''Vases''', ''Horticulturist'' 3, no. 1 (July 1848): 40, figs. 7–11. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1819.jpg|Anonymous, “A Gothic '''vase''',” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 424, fig. 69. | |
| − | Gardening ( | ||
| − | + | File:0388.jpg|Anonymouse, '''Vase''', in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 425, fig. 72. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | File:0389.jpg|Anonymous, “A pleasing [[Rustic_style|rustic]] '''vase''',” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 526, fig. 74. | ||
| − | + | File:0403.jpg|Anonymous, “Tazza [[Fountain]],” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 471, fig. 93. | |
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | + | ===Associated=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1175.jpg|Anonymous, "A fine terra-cotta '''vase'''," [[A. J. Downing]], “Remarks on the Different Styles of Architecture,” ''American Gardeners’ Magazine'' vol. 2, no. 8 (August 1836): 286, fig. 11. | |
| − | + | File:1118.jpg|W. H. Bartlett, "Undercliff Near Cold-Spring. (The [[Seat]] of General George P. Morris)," in Nathaniel Parker Willis, ''American Scenery; or, Land, [[Lake]] and River Illustrations of Transatlantic Nature'' (1840), vol. 2, pl. 11. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0394.jpg|Anonymous, "The [[Conservatory]]," [[Montgomery Place]], in [[A. J. Downing]], ed., ''Horticulturist'' 2, no. 4 (October 1847): 159, fig. 28. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0942.jpg|Anonymous, "Plan of a Suburban Garden," in [[A. J. Downing]], ed., ''Horticulturist'' 3, no. 8 (February 1849): pl. opp. 353. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0350.jpg|[[Alexander Jackson Davis]], "[[View]] in the Grounds at Blithewood," in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), frontispiece. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0370.jpg|Anonymous, "The [[Geometric style]], from an old print," in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 62, fig. 14. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Attributed=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0259.jpg|The Gansevoort Limner (possibly Pieter Vanderlyn), ''Young Lady with a Fan'', 1737. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0191.jpg|[[Charles Willson Peale]], ''Margaret Tilghman Carroll'', c. 1770. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0966.jpg|Charles Bulfinch, Preliminary study for the Elias Hasket Derby House, c. 1795. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0274.jpg|Ralph Earl, ''Houses Fronting New Milford Green'', 1796. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0714.jpg|Anonymous, ''Memorial to Daniel Ma–'', c. 1810. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0001.jpg|George Ropes, ''Salem [[Common]] on Training Day'', 1808. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0251.jpg|Charles Codman, ''Kalorama'', 1821. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0517.jpg|Joshua Tucker, ''South East [[View]] of Greenvill[e], S.C.'', possibly 1825. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1216.jpg|[[Anthony St. John Baker]], [[Mount]] Airy, Virginia; northeast front, 1827, in ''Mémoires d’un voyageur qui se repose'' (1850), part IV, 520A. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:2014.jpg|[[Anthony St. John Baker]], "Front [[View]] of [[Mount]] Airy, Virginia," 1827, in ''Mémoires d’un voyageur qui se repose'' (1850), part IV, 520A. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1247.jpg|[[Alexander Jackson Davis]], ''Villa for David Codwise, near New Rochelle, NY (project; elevation and four plans)'', 1835. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1173.jpg|Anonymous, The Diploma for the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society, c. 1836, in ''Yearbook of the Pennsylvania Horticultural Society'' (1956), frontispiece. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1840.jpg|[[J. C. Loudon]], "Garden Front of Cheshunt Cottage," in ''The Gardener's Magazine'' 15, no. 117 (December 1839): 669, fig. 174. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1477.jpg|Anonymous, Honorary membership certificate for Nicholas Biddle in “The Horticultural Association of the Valley of the Hudson” [detail], June 1839. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0852.jpg|[[Alexander Jackson Davis]], "The [[Conservatory]]," [[Montgomery Place]], c. 1839. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0520.jpg|Anonymous, ''[[Beehive]]s in the Garden'', c. 1840. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0525.jpg|William E. Winner, ''Garden Scene Near Philadelphia'', c. 1840. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0891.jpg|Edwin Whitefield, Sketch of Joseph H. Jennings’ House, 1841—44. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1911.jpg|James Smillie (artist), John A. Rolph (engraver), “Ocean Hill,” in Nehemiah Cleaveland, ''Green-Wood Illustrated'' (1847), opp. 15. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0583.jpg|Lewis Miller, "For a Lady's Album. . . ," in ''Orbis Pictus'' (c. 1849), 125. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0704.jpg|Lewis Miller, "Laurel Hill [[Cemetery/Burying ground/Burial ground|Cemetery]], Philadelphia, September 15" [detail], September 15, 1856. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0218.jpg|Augustus Weidenbach, ''[[Belvedere]]'', c. 1858. | |
| + | |||
| + | File: 2263.jpg|MacKay, ''Catherine Brower'', 1791, oil on canvas. Gift of Edgar William and Bernice Chrysler Garbisch, 1956.13.5, [https://www.nga.gov/collection/art-object-page.43633.html National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.] | ||
| + | |||
| + | File: 2300.jpg|Pavel Petrovich Svinin, ''A Country Residence, Possibly General Moreau's Country House at Morrisville, Pennsylvania '', 1811–ca. 1813. | ||
| + | |||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| − | < | + | <hr> |
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
| Line 511: | Line 254: | ||
[[Category: Keywords]] | [[Category: Keywords]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Garden Ornaments/Embellishments]] | ||
Latest revision as of 19:23, August 12, 2021
History



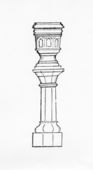
The term vase typically referred to a freestanding, symmetrical vessel having a wider mouth than foot [Fig. 1], although some British pattern books included types with narrow mouths and elaborate lids [Fig. 2]. If fitted with a foot or pedestal set on either a small base or plinth, the vessel sometimes was referred to as an urn. Throughout history, ashes of the dead have been deposited in urns, giving them symbolic importance. Frequently urns were used for memorials and monuments, especially in cemeteries. In the context of the designed landscape, treatise writers often strongly recommended that the vase be placed on top of a pedestal or plinth so that it would be easily visible. A. J. Downing elaborated upon this point in an 1836 article about architecture and at greater length in his 1849 treatise, when he explained that without such a placement, the vase would appear as a temporary, accidental introduction to the landscape. A permanent base, in his opinion, gave the vase the “character of art, at once more dignified and expressive of stability” [Fig. 3].
Vases functioned primarily as ornamentation and were associated with a number of garden features. In his eighteenth-century treatise, Antoine-Joseph Dezallier d’Argenville suggested that vases could be used to decorate parterres, placed amidst planting features (such as groves) or in water features (such as basins), situated at the termination of walks and vistas, or housed within structures (such as porticos and arbors).
Vases continued to be featured in ornamental landscapes well into the 19th century, despite many changes in garden design. A painting of Kalorama, for example, depicts a vase at the center of the view [Fig. 4]. The connection between vases and water features continued as well. Downing’s texts, for example, contain numerous references to vases as fountains. The strategic placement of vases in pleasure grounds also endured. At the early 19th-century estate of Blithewood in Dutchess County, New York, vases of grey Maltese stone (which Downing praised for its ability to harmonize with vegetation) were used throughout the pleasure grounds and, in particular, at the corners of adjoining walks. Vases were also used at the termination of walks, where they served as visual focal points as in a suburban garden design described in 1848 in the Horticulturist.
Treatise authors from different periods agreed that the vase should never be placed far from the house. Thomas Whately, in his 1770 treatise, insisted that the vase “attend the mansion, and trespass a little upon the garden.” In 1849 Downing reiterated Whately's idea, explaining that since the vase was a “highly artificial and architectural” object, it must be situated in the pleasure ground in such a manner that it would always “appear in some way connected with buildings, or objects of a like architectural character.” He cautioned further that vases be used judiciously. If placed “indiscriminately. . . where they have really no place, but interfere with the quiet character of surrounding nature,” vases ran the danger of destroying the “unity of expression” that Downing and others sought.
The function and placement of the vase was closely connected to its style and form. As several treatise writers counseled, vases should be stylistically consistent with their settings and, when placed near the house, should reflect the architectural character of the structure, such as Gothic, Grecian, Roman, or Italianate styles. In nineteenth-century treatises, vases in the classical or ancient style emerged as the most popular. A favored model was the Warwick Vase, a carved and decorated white marble vase from Hadrian’s Villa. The vase was recovered from the Roman site in 1770 by the Englishman William Hamilton and was subsequently taken to England by his nephew, George, Earl of Warwick. At Montgomery Place, designed by Alexander Jackson Davis and Downing in the 1840s, a Warwick-style vase was placed in the center of the flower garden [Fig. 5]. In 1849, Downing described the popular option of the rustic-style vase, in which the vessel was made out of the “branches and sections of trees with the bark attached.”

Outdoor vases were usually large in scale, two to three feet in height. They could be composed of a variety of materials, such as cast-brass, lead gilt, marble, stone and stucco, according to Dezallier d’Argenville. Downing, writing nearly one hundred and fifty years later, gave an equally wide-ranging list, including stone, artificial stone, plaster, and Roman cement. He also cited inexpensive materials intended to imitate luxury materials, such as terra-cotta and English Staffordshire, which could be treated to emulate marble. Downing's allusion to Staffordshire pottery suggests the near-dominant presence of refined British pottery in America. Nevertheless, he mentioned several American manufacturers that produced vases and noted especially such New York manufacturers as the Salamander Works, the Garnick Company, and Coffee’s Manufactory.
Vases were also used as plant containers, as indicated in Augustus Weidenbach’s c. 1858 painting of the garden at Belvedere in Baltimore [Fig. 6], or in C. M. Hovey's 1839 description of a greenhouse or conservatory. Nevertheless, large-scale, ornamental vases were often regarded as works of art, and, therefore, as J. C. Loudon argued, cited by Downing in 1849, they should not be reduced to the level of “a mere garden flower-pot.”
—Anne L. Helmreich
Texts
Usage
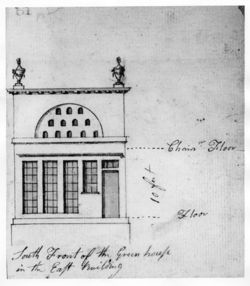
- McIntire, Samuel, June 8, 1795, describing a statement of account with Elias Hasket Derby (quoted in Kimball 1940: 74)[1]
“1793 Dec 4th to Sundrie Drawings for
Summer Houses @ 24/£1: 4: 1794 Apl 25 to Carving 4 Vases for
the Summer House at 18/s each3: 18: July to Building the Summer
House at the Farm @ 100:0:0
to Extra work on the Same,
Viz., finishing four Closets
@20/each 4: 0:0” [Fig. 7]
- Ingraham, Joseph Holt, 1835, describing a plantation near New Orleans, LA (1:243)[2]
- “Passing from this plantation scene through the airy hall of the dwelling, which opened from piazza to piazza through the house, to the front gallery, whose light columns were wreathed with the delicately leaved Cape-jasmine, rambling woodbine and honeysuckle, a lovelier and more agreeable scene met my eye. I stood almost embowered in the foliage of exotics and native plants, which stood upon the gallery in handsome vases of marble and China-ware. The main avenue opened a vista to the river through a paradise of althea, orange, lemon, and olive trees, and groves and lawns extended on both sides of this lovely spot, ‘Where Flora’s brightest broidery shone,’ terminating at the villas of adjoining plantations.”
- Willis, Nathaniel Parker, 1840, describing Undercliff, seat of General George P. Morris, near Cold-Spring, NY (1840; repr. 1971: 233)[3]
- “In front, a circle of greensward is refreshed by a fountain in the centre, gushing from a Grecian vase, and encircled by ornamental shrubbery; from thence a gravelled walk winds down a gentle declivity to a second plateau, and again descends to the entrance of the carriage road, which leads upwards along the left slope of the hill, through a noble forest, the growth of many years, until suddenly emerging from its sombre shades, the visitor beholds the mansion before him in the bright blaze of day.” [Fig. 8]
- Hovey, C. M. (Charles Mason), November 1841, describing Highland Place, estate of A. J. Downing, Newburgh, NY (Magazine of Horticulture 7: 405)[4]
- “7. Large palms in pots, or Maltese vases, or vases made of artificial stone, set on the turf. In the introduction of vases, it should always be remembered that the vase should not be set down immediately on the turf, but upon a plinth. . .
- “8. Rustic basket, for flowers, as represented in the engraving just referred to. These are very easily made. Mr. Downing has given a figure of one, in his Treatise on Landscape Gardening, where he states they may be made in the following manner:—An octagon box serves as the body or frame of the vase; on this, pieces of birch and hazel, (small split limbs, covered with the bark,) are nailed closely, so as to form a sort of mosaic covering to the whole exterior.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, October 1847, describing Montgomery Place, country home of Mrs. Edward (Louise) Livingston, Dutchess County, NY (quoted in Haley 1988: 52)[5]
- “Passing under neat and tasteful archways of wirework, covered with rare climbers, we enter what is properly
- “THE FLOWER GARDEN.
- “In the centre of the garden stands a large vase of the Warwick pattern; others occupy the centres of parterres in the midst of its two main divisions, and at either end is a fanciful light summer-house, or pavilion, of Moresque character.”

- Downing, Andrew Jackson, 1849, describing Blithewood, seat of Robert Donaldson, Dutchess County, NY (1849; repr., 1991: 425)[6]
- “At Blithewood, the seat of R. Donaldson, Esq., on the Hudson, a number of exquisite vases may be seen in the pleasure-grounds, which are cut in Maltese stone. These were imported by the proprietor, direct from Malta, at very moderate rates, and are not only ornamental, but very durable. Their color is a warm shade of grey which harmonizes agreeably with the surrounding vegetation.” [Fig. 9]
- Twain, Mark, October 26, 1853, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (quoted in Gibson 1988: 2)[7]
- “We arrived at Fairmount. . . Seeing a park at the foot of the hill, I entered—and found it one of the nicest little places about. Fat marble Cupids, in big marble vases, squirted water upward incessantly.”
Citations
- Dézallier d’Argenville, Antoine-Joseph, 1712, The Theory and Practice of Gardening (1712; repr., 1969: 75–76)[8]
- “STATUES and Vases contribute very much to the Embellishment and Magnificence of a Garden, and extremely advance the natural Beauties of it. They are made of several Forms, and different Materials; the richest are those of Cast-Brass, Lead gilt, and Marble; the ordinary Sort are of common Stone, or Stucco. . .
- “THE usual Places of Figures and Vases are along the Palisades, in the Front, and upon the Sides of a Parterre; in the Niches and Sinkings of Horn-beam, or of Lattice-work made for that Purpose. In Groves, they are placed in the Center of a Star, or S. Andrew’s Cross; in the Spaces between the Walks of a Goose-foot, in the Middle of Halls and Cabinets, among the Trees and Arches of a Green-Gallery, and at the Head of a Row of Trees, or Palisades, that stand free and detached. They are also put at the lower End of Walks and Vistas, to set them off the better; in Porticos, and Arbors of Trellis-work; in Basons, Cascades, &c. In general, they do well every where; and you can scarce have too many of them in a Garden: But, as in the Business of Sculpture, it should be excellent, as well as in Painting and Poesy [sic] (which are its two Sisters).”

- Gibbs, James, 1728, A Book of Architecture (1728: xxi, xxv)[9]
- “Three Designs for Columns, proper for publick Places or private Gardens; viz. a plain Dorick Column upon its Pedestal with a Vase a top, a fluted Column properly adorn’d, and a Rustick frosted Column, with a Figure a-top, as I have made them for several Gentlemen. The Proportions of them are mark’d upon an upright Line, divided into so many Diameters of the Column for the Height. . .
- “Three Designs for Vases, done for the Right Honourable the Earl of Oxford. There are two Vases well executed in Portland Stone according to the middle Draught, which are set upon two large Peers on each side of the principal Walk in the Garden at Wimpole in Cambridgeshire. . . [Fig. 10]
- “Fifty four Draughts of Vases, &c. in the Antique manner, made for several persons at different times. Many of them have been executed both in Marble and Metal.”
- Whately, Thomas, 1770, Observations on Modern Gardening (1770; repr., 1982: 138)[10]
- “vases, statues, and termini, are usual appendages to a considerable edifice; as such they may attend the mansion, and trespass a little upon the garden, provided they are not carried so far into it as to lose their connection with the structure.”
- Webster, Noah, 1828, An American Dictionary of the English Language (1828: n.p.)[11]
- “URN. . . A kind of vase of a roundish form, largest in the middle; used as an ornament. Cyc. . .
- “VASE, n. [Fr. from L. vas, vasa, a vessel; It. vaso.]
- “1. A vessel for domestic use, or for use in temples; as a vase for sacrifice, an urn, &c.
- “2. An ancient vessel dug out of the ground or from rubbish, and kept as a curiosity.
- “3. In architecture, an ornament of sculpture, placed on socles or pedestals, representing the vessels of the ancients, as incense-pots, flower-pots, &c. They usually crown or finish facades or frontispieces. Cyc.
- “4. The body of the Corinthian and Composite capital; called also the tambor or drum.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, August 1836, “Remarks on the Fitness of the different Styles of Architecture for the Construction of Country Residences, and on the Employment of Vases in Garden Scenery” (American Gardeners’ Magazine 2: 285–86)[12]
- “It will not be inadvertent to the present hasty remarks to hint at the additional charm which may be produced in highly finished places, especially where the buildings are in the Grecian style, by introducing into the lawns and gardens the classic vase in its different forms, and, if thought desirable, statues also. They serve as it were as a connecting link between so highly artificial an object as a modern villa, and the verdant lawns and gay gardens which surround it. Elevated upon pedestals, and placed at suitable points in the view—on the parapets of terraces near the house—before a group of foliage upon the lawn, and at proper intervals in the garden, they give a classic and elegant air to the whole, which adds greatly to its value. Beautiful in their forms, contrasting finely with the deep green of vegetation, and leading the eye gradually from their own sculptured beauty to the architectural symmetry of the building, of which they form as it were a continuous though detached part, amalgamating it with the grounds in which it is placed—their effect can only be appreciated beforehand by those who have studied the excellent effect produced by their introduction into the scene.
- “Another reason which may be offered for the introduction of vases into architectural and garden scenery is ‘the gratification which such objects afford to the man of intelligence and taste. There are, perhaps, few objects, next to the human figure, which afford as many interesting historical associations as the vase. It may truly be said to be the first and last production of the plastic art. The first utensil formed by man, in the dawn of civilization in every country, is a vessel or vase for holding water; and that on which the highest resources of art are bestowed, in ages of the greatest refinement, is a vase or vessel for holding wine. In the first case, it is hollowed out of a gourd, or rudely shaped of clay, and dried in the sun; and, in the latter case, it is manufactured of costly metals or precious stones; or, if of common materials, such as stone, earthenware or glass, it is rendered valuable by the taste and skill bestowed on its form and ornaments. The history of every country may be traced by its vases no less than by its coins; and the history of all countries is set before us in the vases of all countries.’ [Loudon, X. 494.]”
- Hovey, C. M. (Charles Mason), January 1839, “Notes on Gardens and Nurseries” (Magazine of Horticulture 5: 29)[13]
- “The beauty of vases in garden scenery has been already urged by our correspondent, Mr. Downing, (Vol. II, p. 281,) and we had intended to add something to his remarks, ourselves, by the way of impressing the subject more upon the attention of our readers. . .
- “Surely we need not say any thing further to show how much they would add to the beauty of the garden, or the elegance of the conservatory. In either place, they are objects too inviting not to be found in every garden. These vases are easily filled with handsome plants, well suited to the situation, and the following might compose, in part, the group for the green-house.”
- Rusticus [pseud.], August 1846, “Design for a Rustic Gate” (Horticulturist 1: 72)[14]
- “Indeed, rustic work of all kinds is extremely pleasing in any situation where there is any thing like a wild or natural character; or even where there is a simple and rustic character. In the immediate proximity of a highly finished villa, it strikes me that rustic work, such as arbors, fences, flower baskets and the like, are rather out of place. The sculptured vase of marble, or terra cotta, would appear to be the most in keeping with an elegant place of the first class; that is to say, for all situations very near the house. In wooded walks, or secluded spots, rustic work looks well always.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, July 1848, “Ornamental Vases and Chimney Tops” (Horticulturist 3: 40)[15]
- “There are few objects that may, with so much good effect, be introduced into the scenery of pleasure grounds, surrounding a tasteful villa, as the vase, in its many varied forms. The terra cotta vases of the Garnkirk company exhibit pleasing forms, and a soft mellow shade of colour, which harmonizes admirably with the hue of foliage and turf. From among the variety manufactured by them, we have selected a few, of which we here present engravings. . .
- “To set down a vase upon the earth, or the lawn, without any pedestal, is to give it a temporary character, and to rob it of that dignity and importance which it gains, both to the eye and the reason, by being placed on a firm and secure pedestal. . .
- “Looking at the vase in an artistical point of view, it is considered as performing the office of uniting the architecture and the grounds of a complete country residence. It is the architectural idea, carried a little beyond the house, and shows that the same feeling of taste and embellishment reigns in both departments of the residence. It will be easily understood from this, that the most suitable place for vases is in highly kept portions of the pleasure ground, near the house, where the vases may be seen in connexion with it; or, at least, where the architecture of the building harmonizes with the highly artificial forms of the vase. The simplest cottage may have its vase; but, where the building is small, the rustic vase, made of bits of wood, and filled with flowering plants, is in better keeping than those made of any more highly artificial materials.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, 1849, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849: 423–27, 471, 473)[6]
- “Where there is a terrace ornamented with urns or vases, and the proprietor wishes to give a corresponding air of elegance to his grounds, vases, sundials, etc., may be placed in various appropriate situations, not only in the architectural flower-garden, but on the lawn, and through the pleasure-grounds in various different points near the house. We say near the house, because we think so highly artificial and architectural an object as a sculptured vase, is never correctly introduced unless it appear in some way connected with buildings, or objects of a like architectural character. To place a beautiful vase in a distant part of the grounds, where there is no direct allusion to art, and where it is accompanied only by natural objects, as the overhanging trees and the sloping turf, is in a measure doing violence to our reason or taste, by bringing two objects so strongly contrasted, in direct union. But when we see a statue or a vase placed in any part of the grounds where a near view is obtained of the house (and its accompanying statues or vases), the whole is accounted for, and we feel the distant vase to be only part of, or rather a repetition of the same idea,—in other words, that it forms part of a whole, harmonious and consistent.
- “Vases of real stone, as marble or granite, are decorations of too costly a kind ever to come into general use among us. Vases, however, of equally beautiful forms, are manufactured of artificial stone, of fine pottery, or of cast iron, which have the same effect, and are of nearly equal durability, as garden decorations.
- “A vase should never, in the open air, be set down upon the ground or grass, without being placed upon a firm base of some description, either a plinth or a pedestal. Without a base of this kind it has a temporary look, as if it had been left there by mere accident, and without any intention of permanence. Placing it upon a pedestal, or square plinth (block of stone), gives it a character of art, at once more dignified and expressive of stability. Besides this, the pedestal in reality serves to preserve the vase in a perpendicular position, as well as to expose it fairly to the eye, which could not be the case were it put down, without any preparation, on the bare turf or gravel.
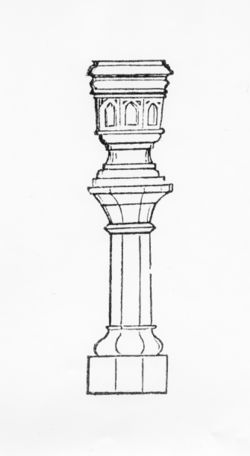
- “Figure 69 is. . . Gothic. . . These with many other elegant vases and urns are manufactured in an artificial stone, as durable as marble, by Austin of London, and together with a great variety of other beautiful sculpturesque decorations, may be imported at very reasonable prices. . . [Fig. 11]
- “These vases, when colored to imitate marble or other stone, are extremely durable and very ornamental. As yet, we are unable to refer our readers to any manufactory here, where these articles are made in a manner fully equal to the English; but we are satisfied, it is only necessary that the taste for such articles should increase, and the consequent demand, to induce our artisans to produce them of equal beauty and of greater cheapness. . .
- “Large vases are sometimes filled with earth and planted with choice flowering plants, and the effect of the blossoms and green leaves growing out of these handsome receptacles, is at least unique and striking Loudon objects to it in the case of an elegant sculptured vase, ‘because it is reducing a work of art to the level of a mere garden flower-pot, and dividing the attention between the beauty of the form of the vase and of its sculptured ornaments, and that of the plant which it contains.’ This criticism is a just one in its general application, especially when vases are considered as architectural decorations. Occasional deviations, however, may be permitted, for the sake of producing variety, especially in the case of vases used as decorations in the flower-garden.

- “A very pretty and fanciful substitute for the sculptured vase, and which may take its place in the picturesque landscape, may be found in vases or baskets of rustic work, constructed of the branches and sections of trees with the bark attached. Figure 74 is a representation of a pleasing rustic vase which we have constructed without difficulty. A tripod of branches of trees forms the pedestal. An octagonal box serves as the body or frame of the vase; on this, pieces of birch and hazel (small split limbs covered with the bark) are nailed closely, so as to form a sort of mosaic covering to the whole exterior. Ornaments of this kind, which may be made by the amateur with the assistance of a common carpenter, are very suitable for the decoration of the grounds and flower-gardens of cottages or picturesque villas. An endless variety of forms will occur to an ingenious artist in rustic work, which he may call in to the embellishment of rural scenes, without taxing his purse heavily. . . [Fig. 12]
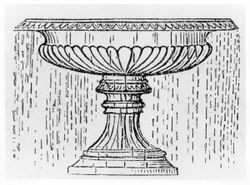
- “Weeping, or Tazza Fountains, as they are called, are simple and highly pleasing objects, which require only a very moderate supply of water compared with that demanded by a constant and powerful jet. The conduit pipe rises through and fills the vase, which is so formed as to overflow round its entire margin. Figure 93 represents a beautiful Grecian vase for tazza fountains. The ordinary jet and the tazza fountain may be combined in one, when the supply of water is sufficient, by carrying the conduit pipe to the level of the top of the vase, from which the water rises perpendicularly, then falls back into the vase and overflows as before. . . [Fig. 13]
- “Unity of expression is the maxim and guide in this department of the art, as in every other. Decorations can never be introduced with good effect, when they are at variance with the character of surrounding objects. A beautiful and highly architectural villa may, with the greatest propriety, receive the decorative accompaniments of elegant vases, sundials, or statues, should the proprietor choose to display his wealth and taste in this manner; but these decorations would be totally misapplied in the case of a plain square edifice, evincing no architectural style in itself.
- “In addition to this, there is great danger that a mere lover of fine vases may run into the error of assembling these objects indiscriminately in different parts of his grounds, where they have really no place, but interfere with the quiet character of surrounding nature. He may overload the grounds with an unmeaning distribution of sculpturesque or artificial forms, instead of working up those parts where art predominates in such a manner, by means of appropriate decorations, as to heighten by contrast the beauty of the whole adjacent landscape.”
Images
Inscribed
James Gibbs, “Three Designs for Vases,” in A Book of Architecture (1728), pl. 138.
James Gibbs, Nine of “Fifty four Draughts of Vases,” in A Book of Architecture (1728), pl. 139.
Samuel McIntire, South Front of the Green house in the East Building, Elias Hasket Derby House, c. 1799.
J. C. Loudon, “Rustic arch and vase,” in The Suburban Gardener (1838), 581, fig. 231.
J. C. Loudon, “Hermit's Seat, and Classical Vase,” Cheshunt Cottage, in The Gardener's Magazine 15, no. 117 (December 1839): 664, fig. 172.
Anonymous, “Ground Plan of a portion of Downing's Botanic Gardens and Nurseries,” in Magazine of Horticulture 7, no. 11 (November 1841): 404. "7. Large palms in pots, or Maltese vases, or vases made of artificial stone, set on the turf (. . .) 8. Rustic basket, for flowers. . ."
Anonymous, “A pair of tozza [sic] vases, for a fountain,” in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 3, no. 1 (July 1848): 42, fig. 13.
Anonymous, “A Gothic vase,” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), 424, fig. 69.
Anonymouse, Vase, in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), 425, fig. 72.
Anonymous, “A pleasing rustic vase,” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), 526, fig. 74.
Anonymous, “Tazza Fountain,” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), 471, fig. 93.
Associated
Anonymous, "A fine terra-cotta vase," A. J. Downing, “Remarks on the Different Styles of Architecture,” American Gardeners’ Magazine vol. 2, no. 8 (August 1836): 286, fig. 11.
Anonymous, "The Conservatory," Montgomery Place, in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 2, no. 4 (October 1847): 159, fig. 28.
Anonymous, "Plan of a Suburban Garden," in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 3, no. 8 (February 1849): pl. opp. 353.
Alexander Jackson Davis, "View in the Grounds at Blithewood," in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), frontispiece.
Anonymous, "The Geometric style, from an old print," in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849), 62, fig. 14.
Attributed
Charles Willson Peale, Margaret Tilghman Carroll, c. 1770.
George Ropes, Salem Common on Training Day, 1808.
Joshua Tucker, South East View of Greenvill[e], S.C., possibly 1825.
Anthony St. John Baker, Mount Airy, Virginia; northeast front, 1827, in Mémoires d’un voyageur qui se repose (1850), part IV, 520A.
Anthony St. John Baker, "Front View of Mount Airy, Virginia," 1827, in Mémoires d’un voyageur qui se repose (1850), part IV, 520A.
Alexander Jackson Davis, Villa for David Codwise, near New Rochelle, NY (project; elevation and four plans), 1835.
J. C. Loudon, "Garden Front of Cheshunt Cottage," in The Gardener's Magazine 15, no. 117 (December 1839): 669, fig. 174.
Alexander Jackson Davis, "The Conservatory," Montgomery Place, c. 1839.
Anonymous, Beehives in the Garden, c. 1840.
Lewis Miller, "Laurel Hill Cemetery, Philadelphia, September 15" [detail], September 15, 1856.
Augustus Weidenbach, Belvedere, c. 1858.
MacKay, Catherine Brower, 1791, oil on canvas. Gift of Edgar William and Bernice Chrysler Garbisch, 1956.13.5, National Gallery of Art, Washington, D.C.
Notes
- ↑ Fiske Kimball, Mr. Samuel McIntire, Carver, the Architect of Salem (Portland, ME: Southworth-Anthoensen, 1940), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Joseph Holt Ingraham, The South-West, 2 vols. (New York: Harper, 1835), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Nathaniel Parker Willis, American Scenery; Or, Land, Lake and River Illustrations of Transatlantic Nature (London: G. Virtue, 1840), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Charles Mason Hovey, “Select Villa Residences, with Descriptive Notices of Each; Accompanied with Remarks and Observations on the Principles and Practice of Landscape Gardening: Intended with a View to Illustrate the Art of Laying Out, Arranging, and Forming Gardens and Ornamental Grounds,” Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs 7, no. 11 (November 1841): 401–11, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Jacquetta M. Haley, ed., Pleasure Grounds: Andrew Jackson Downing and Montgomery Place (Tarrytown, NY: Sleepy Hollow Press, 1988), view on Zotero.
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America, 4th ed. (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Jane Mork Gibson, “The Fairmount Waterworks,” Bulletin, Philadelphia Museum of Art 84 (1988): 5–40, view on Zotero.
- ↑ A.-J. (Antoine Joseph) Dézallier d’Argenville, The Theory and Practice of Gardening; Wherein Is Fully Handled All That Relates to Fine Gardens, . . . Containing Divers Plans, and General Dispositions of Gardens; . . . , trans. by John James (London: Geo. James, 1712), view on Zotero.
- ↑ James Gibbs, A Book of Architecture, Containing Designs of Buildings and Ornaments (London: Printed for W. Innys et al., 1728), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Thomas Whately, Observations on Modern Gardening, 3rd ed. (London: Garland, 1982), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Noah Webster, An American Dictionary of the English Language, 2 vols. (New York: S. Converse, 1828), view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. Downing, “Remarks on the Fitness of the different Styles of Architecture for the Construction of Country Residences, and on the Employment of Vases in Garden Scenery,” American Gardeners’ Magazine, and Register of Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Horticulture and Rural Affairs 2, no. 8 (August 1836): 281–86, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Charles Mason Hovey, “Notes on Gardens and Nurseries,” Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs 5, no. 1 (January 1839): 59–65, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Rusticus [pseud.], “Design for a Rustic Gate,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 1, no. 2 (August 1846): 72–73, view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. Downing, “Ornamental Vases and Chimney Tops,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 3, no. 1 (July 1848): 37–43, view on Zotero.