Difference between revisions of "Geometric style"
(→Texts) |
V-Federici (talk | contribs) m (→Images) |
||
| (51 intermediate revisions by 8 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | See also: [[Ancient style]] | ||
| + | |||
==History== | ==History== | ||
| + | [[File:0370.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 1, Anonymous, “The Geometric style, from an old print,” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 62, fig. 14. ]] | ||
| + | [[File:0017.jpg|thumb|Fig. 2, Anonymous, Illustration of Williamsburg buildings, flora and fauna. Modern impression taken from the original 1740s copperplate [Bodleian Plate re-strike].]] | ||
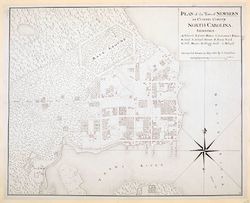
| + | The term geometric style came into use only when it was necessary to make a distinction between the traditional mode of laying out gardens and the newer [[Modern_style|modern]], [[Natural style|natural]], or irregular style. Geometric, ancient, and formal were terms used interchangeably to describe gardens laid out symmetrically in straight lines, with strong axial circulation paths and geometrically regular [[bed]]s [Fig. 1] (see [[Ancient style]]). The style was associated with French, Anglo-Dutch, and Italian traditions of gardening (see [[Dutch style]] and [[French style]]). In America, the geometric style continued to be popular long after the [[Natural style|natural]] or modern style was introduced. As part of a larger landscaped garden, the flower garden was a feature that lent itself to regular shapes. Early public buildings such as the Governor’s Palace in Williamsburg, Virginia [Fig. 2], and Governor’s House in New Bern, North Carolina [Fig. 3], were laid out in a geometric style although, again, the term was used only after the modern style had become popular. The geometric style continued to be used in public places because of its long-standing association with centers of government. | ||
| − | + | [[File:0248.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 3, Claude Joseph Sauthier, ''A Plan of the Town of Newbern in Craven County, North Carolina'', 1769.]] | |
| + | [[File:1675.jpg|thumb|Fig. 4, Anonymous, Vignette of contrasting garden styles, in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 17. ]] | ||
| + | The geometric style was also used well into the 19th century for domestic landscapes throughout the colonies. Often found in town gardens, this style suited the orthogonal layout of street plans and small lots.<ref>For a discussion of geometric layouts of Louisiana gardens, see Suzanne Turner, “Roots of a Regional Garden Tradition: The Drawings of the New Orleans Notarial Archives,” in ''Regional Garden Design in the United States'', ed. T. O’Malley and M. Treib (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1995), 163–90, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/BQB5TZTU view on Zotero].</ref> It was equally prevalent in the [[plantation]] landscape throughout the South [Fig. 4].<ref>For a discussion of the geometrical principles of plantation layouts, see C. Allan Brown, “Eighteenth-Century Virginia Plantation Gardens: Translating an Ancient Idyll,” in ''Regional Garden Design in the United States'', 125–62, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/IT2UBCXX view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| − | + | [[Andrew Jackson Downing|A. J. Downing]]’s description of [[Lemon Hill]] in Philadelphia explained the symmetry, uniformity, and high art of the geometric mode, listing the standard features of the style with its artificial [[plantation]]s and highly regularized gardens. ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849) contains a miniature vignette of the two main modes of garden design [Fig. 4]. Downing’s descriptions of earlier American gardens, such as [[Lemon Hill]], were respectful from a historical point of view. However, he denigrated his compatriots who continued to practice this mode. His English contemporary, [[Jane Loudon]], whose work he was the first to publish in this country, described the geometric style succinctly without the negative tone found in garden writings such as Downing’s. Mrs. Loudon offered the style as an alternative, suitable and appropriate wherever symmetrical architecture existed. The term “artificial” was often used synonymously with “geometric,” especially when opposed to the so-called [[Natural style|natural]] (or [[modern style]]), as in the quotations of George Watterston and Downing. | |
| − | + | —''Therese O’Malley'' | |
| − | + | <hr> | |
==Texts== | ==Texts== | ||
| − | |||
===Usage=== | ===Usage=== | ||
| + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], January 1837, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States” (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 3: 8)<ref>Andrew Jackson Downing, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States,” ''Magazine of Horticulture'' 3 (1837): 1–10, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/HPNHTESI view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“The finest single example of [[landscape gardening]], in the [[modern style]], is at [[Dr. Hosack]]’s [[seat]], [[Hyde Park (on the Hudson River, NY)|Hyde Park]], and the best specimens of the ancient or '''geometric style''' may probably be met with in the neighborhood of Philadelphia.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *W., February 1842, describing Lowell Cemetery, Lowell, MA (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 8: 49)<ref>W., “An Account of the Lowell Cemetery, Its Situation, Historical Associations, and Particular Description,” ''Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs'' 8 (1842): 47–50, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/UKZS86F6 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | in | + | :“In laying out these grounds, the skill of the designer has been displayed, in combining somewhat the ‘ancient or '''geometric style'''’ with the [[Natural_style|natural]] or irregular. In some parts, the regular forms and right lines are well adapted to the location of the ground, while in others, the varied and gradually curving forms give an air of grandeur and boldness, and in combining these with the natural scenery, cannot fail to call forth, in the minds of visitors, impressions of love and veneration.” |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | with in the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], 1849, describing [[Lemon Hill]], estate of [[Henry Pratt]], Philadelphia (1849; repr., 1991: 43)<ref>A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America'', 4th ed. (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/K7BRCDC5 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“''[[Lemon Hill]]'', half a mile above the Fairmount waterworks of Philadelphia, was, 20 years ago, the most perfect specimen of the '''geometric''' mode in America, and since its destruction by the extension of the city, a few years since, there is nothing comparable with it, in that style, among us. All the symmetry, uniformity, and high art of the old school, were displayed here in artificial [[plantation]]s, formal gardens with [[trellis]]es, [[grotto]]es, spring-houses, [[temple]]s, [[statue]]s, and [[vase]]s, with numerous [[pond]]s of water, [[jets-d’eau]], and other water-works, [[parterre]]s and an extensive range of [[hothouse]]s. The effect of this garden was brilliant and striking; its position, on the lovely banks of the Schuylkill, admirable; and its liberal proprietor, [[Henry Pratt|Mr. Pratt]], by opening it freely to the public, greatly increased the popular taste in the neighborhood of that city.” | |
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | and | ||
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Citations=== | ===Citations=== | ||
| + | *[[J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon|Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius)]], 1826, ''An Encyclopaedia of Gardening'' (1826: 1005–6, 1020–21)<ref>J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, ''An Encyclopaedia of Gardening; Comprising the Theory and Practice of Horticulture, Floriculture, Arboriculture, and Landscape-Gardening'', 4th ed. (London: Longman et al., 1826), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/KNKTCA4W view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“7205. ''In planting in the '''geometric style''''', the first consideration is the nature of the whole or general design; and here, as in the ground, '''geometric''' forms will still prevail, and while the masses reflect forms from the house, or represent [[square]]s, triangles, or trapeziums, the more minute parts, characterised by lines rather than forms, such as [[avenue]]s, rows, [[clump]]s, and stars, &c. are contained in parallelograms, squares, or circles. In regard to the parts, masses and [[avenue]]s should extend from the house in all directions, so far as to diffuse around the character of design; and as much farther in particular directions as the nature of the surface admits of, the distant beauties suggest, and the character of the mansion requires. In disposing these masses, whether on a flat or irregular surface, regard will be had to leave uncovered such a quantity of [[lawn]] or turf as shall, at all events, admit a free circulation of air, give breadth of light, and display the form of the large masses of wood. Uniformity and variety as a whole, and use as well as beauty in the parts, must be kept constantly in [[view]]. [[Avenue]]s, [[alley]]s, and [[vista]]s, should serve as much as possible as roads, [[walk]]s, lines of [[fence]]s, or screens of shelter or shade; but where this is not the case, they should point to some distant beauties, or near artificial objects, to be seen at or beyond their termination. The outer extremities of artificial [[plantation]]s may either join natural [[wood]]s, other artificial scenes, cultivated lands, or barren heaths or [[common]]s. . . | ||
| + | :“7262. ''The [[lawn]]'', or that breadth of mown turf formed in front of, or extending in different directions from, the garden-front of the house, is, in the '''geometric style''', varied by architectural forms, levels, and [[slope]]s; and in the modern by a [[picturesque]] or painter-like disposition of groups, placed so as to connect with the leading masses, and throw the [[lawn]] into an agreeable shape or shapes. In very small villas the lawn may embrace the garden or principal front of the house, without the intervention of [[terrace]]-scenery, and may be separated from the [[park]], or park-like field, by a light wire [[fence]]; but in more extensive scenes it should embrace a [[terrace]], or some avowedly artificial architectural basis to the mansion, and a sunk wall, as a distant separation, will be more dignified and permanent than any iron [[fence]]. The [[park]] may come close up to the [[terrace]]-garden, especially in a flat situation, or where the breadth of the terrace is considerable. . . | ||
| + | :“7265. ''The [[park]]''. . . In the '''geometric style''', the more distant or concealed parts were subdivided into fields, surrounded by broad stripes or double rows, enclosed in [[wall]]s or [[hedge]]s, and the nearer parts were chiefly covered with [[wood]], enclosing regular surfaces of pasturage.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Anonymous, April 1, 1837, “Landscape Gardening” (''Horticultural Register'' 3: 124)<ref>Anonymous, “Landscape Gardening,” ''Horticultural Register and Gardener’s Magazine'' 3 (April 1837): 121–31, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/TBFISAR7 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“The uniformity produced by straight [[walk]]s and [[alley]]s bordered by regular rows of trees, another characteristic of the old or '''geometrical style''', though pleasing at first, soon becomes tiresome.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:1753.jpg|thumb|Fig. 5, [[J. C. Loudon]], “A Villa Residence of Two Acres, within a regular Boundary, laid out in the Geometrical Style,” in ''The Suburban Gardener'' (1838), 530, fig. 200. ]] | |
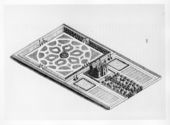
| − | + | *[[J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon|Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius)]], 1838, ''The Suburban Gardener'' (1838: 529–31)<ref>J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, ''The Suburban Gardener, and Villa Companion'' (London: Longman et al., 1838), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/BQVBJ48F view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“''A Villa Residence of Two Acres, within a regular Boundary, laid out in the '''Geometrical Style'''.''—The object in this case is to produce a splendid effect at a moderate expense of annual keeping, but with no regard to profit. The general form of the ground is that of a parallelogram, and its disposition is so clearly shown in the isometrical view. . . that it will require little or no description. The entrance is through a straight [[avenue]] to a flight of steps, which leads to a raised platform on which the house stands. To the right and left of the [[avenue]] are double rows of trees, which may be fruit-bearing kinds, such as the apple, pear, cherry, and plum. Beyond these, on each side, are two small [[kitchen-garden]]s, intended for gooseberries, strawberries, and other small fruits, and for pot-herbs, tart rhubarb, spinach, kidneybeans, and a few such vegetables as are desirable to have always at hand. The house and these [[kitchen-garden]]s occupy about half the entire residence.The other half is laid out in the form of a sunk [[flower-garden]], consisting of a variety of curvilinear [[bed]]s, bordered by a kerb of stone, and surrounded by turf. From the [[terrace]] [[walk]]s there are four descents to this garden, each consisting of a double flight of steps. Each [[bed]] is supposed to be planted with one kind of herbaceous plant, so as to produce large masses of colour. The mode of selecting plants for this purpose, as well as lists of suitable plants, have been already given (p. 217 to p. 226), and further resources will be found in our catalogue. The sloping [[border]] between the sunk area and the [[flower-garden]] may either be planted with low evergreen [[shrub]]s, with roses kept low, or it may be in turf, or in [[rockwork]]: in the latter case, it may be covered with a collection of rock plants. Perhaps the most appropriate disposition of this sloping [[border]] would be to vary it with ornaments of box, on a ground of turf, so as to give it the appearance of an architectural moulding. In the centre there is a [[fountain]]. In situations where so much turf was not desirable, the [[walk]]s between the [[bed]]s might be of gravel or paved; but they will produce the best effect in turf.” [Fig. 5] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | a | ||
| − | is | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *W., M. A., February 1840, “On Flower Beds” (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 6: 52)<ref>M. A. W., “On Flower Beds,” ''Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs'' 6 (February 1840): 51–54, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/6F4WDBVV view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | ( | + | :“It is probably as difficult to fix upon the most suitable plant for the [[edging]] of a flower bed, as it is to determine the best [[shrub]] for a [[hedge]] around fields. For the borders of main [[avenue]]s, or broad [[walk]]s in grounds of considerable extent, box, as recommended, Vol. V., p. 350, is undoubtedly the best; but for small [[parterre]]s, or the flower [[bed]]s in a front door [[yard]], it seems much less suitable. They can commonly be taken in at one glance of the eye, and notwithstanding all that has been said of the artificial or '''geometric style''', it is the proper one for such places; for symmetry, or a perfect balance of corresponding parts, greatly strengthens the impression of such a scene, taken as a whole, or single mass of objects. The [[bed]]s, therefore, will not only be small, but when there is the proper variety in the form of them, some, at least, must have quite acute angles. Box, if thrifty, (and, sickly, it would be an eyesore any where,) soon takes up too much space in breadth.” |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Watterston, George, May 1844, “Landscape Gardening” (1844: 307–8, 310–11)<ref>George Watterston, “Landscape Gardening,” ''Southern Literary Messenger'' 10 (May 1844): 306–15, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/3F6PUXVE view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| + | :“The [[Dutch style]], introduced by William III., and which prevailed in England for about fifty years was not much better, and was distinguished for sloped [[terrace]]s formed of grass, land and water made into regular shapes by art, and adorned with trees in [[pot]]s, or ‘planted alternately and clipped to preserve the most perfect regularity of shape’— and leisure, ‘in trim gardens, took his pleasure.’ ‘The compass and the square,’ says Walpole, ‘were of more use than the nurseryman. The measured [[walk]], the quincunx and the étoile imposed their unsatisfying sameness on every royal and noble garden. Trees were headed and their sides pared away; many French [[grove]]s seem green chests set upon poles. Seats of marble, [[arbor]]s and [[summer house]]s terminated every [[vista]], and symmetry, even when the space was too large to permit its being remarked at one [[view]], was so essential, that, as Pope observed, | ||
| − | + | ::‘[[Grove]] nods to ''[[grove]]'', each [[alley]] has a brother | |
| + | ::And half the platform just reflects the other.’ | ||
| − | + | :This formal, or '''geometric style''' was all the rage at the commencement of the 17th century in those parts of Europe where ornamental gardening prevailed, and the most distinguished artist of that age, if artist he could be called, was ''Le Notre''. . . | |
| − | + | :“In passing from the [[ancient style|ancient]], or '''geometric style''', to the [[Modern_style|modern]], or [[Natural style|natural]], the first improvers fell, perhaps, into an opposite extreme. This is the danger in all sudden transitions. They seemed to conceive that crooked lines, serpentine windings and carelessness were true objects of beauty, and declared that nature ''abhorred a straight line''; and thus fatigued the eye by incessant curves. They did not seem to be aware, that in her sublimest works nature prefers the straight line, as is shown in the apparent horizon of the ocean and the rays of the sun.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | the | ||
| − | is | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Loudon, Jane]], 1845, ''Gardening for Ladies'' (1845: 221–22)<ref>Jane Loudon, ''Gardening for Ladies; and Companion to the Flower-Garden'', ed. A. J. Downing (New York: Wiley & Putnam, 1845), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/3Q5GCH4I view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“'''GEOMETRIC''' GARDENS.—This style of gardening is that in which the shape of the ground, of the [[bed]]s, of the [[walk]]s, and even of the [[shrub]]s, is regular, or symmetrical; such as may be formed on paper by a rule and compass. The ground, if originally flat, is reduced to a general level surface, over which the [[bed]]s, or [[border]]s, are distributed so as to form figures, either simply regular, such as [[square]]s and parallelograms, repeated one after another—or [[square]]s and parallelograms, and circles or ovals, or other curvilinear figures,—so arranged as to be symmetrical; that is to say, that one-half of the figure formed by the whole shall correspond with the other half. When the surface is naturally irregular or on a [[slope]], it is thrown into different levels, which are joined by steep slopes called [[terrace]]s, generally covered with turf, and ascended and descended by stone steps. Each of the levels is laid out either regularly or symmetrically, in the same manner as if the whole were only one [[bed]]; but the figures are of course smaller. Small trees or evergreen [[shrub]]s are distributed among the figures, and especially on each side of the main [[walk]]s; and these trees or [[shrub]]s ought, in strict accordance with the style, to be cut or clipped into regular shapes; such as cones, pyramids, balls, candelabra, [[statue]]s of men or animals, [[arcade]]s, [[column]]s, or other architectural figures. In modern practice, this is generally neglected; but its omission is a defect, for cut trees are as essential to the '''geometric style''', as having the ground cut or shaped into artificial surfaces.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Thomas, John J., April 1848, “The Shrubbery and Flower Garden” (''Cultivator'' 5: 114)<ref>John J. Thomas, “The Shrubbery and Flower Garden,” ''Cultivator, a Monthly Publication, Devoted to Agriculture'' 5, no. 4 (April 1848): 114–16, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/CRVBXUHR/ view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“Nearly all the [[flower garden]]s of the country are laid out in '''geometrical''' lines; a style, it is true much better adapted to the small piece of ground allotted to flowers, than to the larger landscape garden composed of trees, [[lawn]]s, and sheets of water. With a wish however, to encourage a more graceful, pleasing, and [[picturesque]] mode of laying out even the small [[flower garden]] in connexion with the [[shrubbery]], we have given the above plan, which nearly explains itself.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | the | ||
| − | of the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], May 1848, “Design for a Small Flower Garden” (''Horticulturist'' 2: 503)<ref>A. J. Downing, “Design for a Suburban Garden,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 3 (May 1848): 380, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/HNE67CR3 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“The old '''geometric''' [[flower garden]]s, laid out with long [[bed]]s, bordered with box, and separated by stiff gravel [[walk]]s, are fast giving place to those more tasteful combinations of masses of gay, perpetual flowering plants, arranged upon turf, in the arabesque or [[English style]]. | |
| − | + | :“In the former, you have a miscellaneous collection of plants, of all sizes and habits of growth, only a small part of which are seen in bloom at one time; while at almost all seasons naked stalks of plants, and bare dry soil borders, appear here and there, almost in spite of the best efforts of the gardener, to disfigure and mar the general elegance of the scene. | |
| − | + | :“In the latter, you have always the rich setting of the soft green turf, (which, of course mown once a fortnight, is short and velvet-like) and contrasting and enhanced in effect by this, are seen the [[bed]]s of dwarfish plants, grown in masses, so as to give breadth and brilliancy of effect; these being composed only of plants almost perpetually in bloom, unite to form a floral picture, when well managed, as beautiful as the art of gardening will permit.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | and | ||
| − | |||
| − | of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:0997.jpg|thumb|Fig. 6, Anonymous, “Design for a Geometric [[Flower Garden]],” in [[A. J. Downing]], ed., ''Horticulturist'' 2, no. 12 (June 1848): 558, fig. 67.]] | |
| − | + | *Valk, Dr. William W., June 1848, “Design for a Geometric Flower Garden” (''Horticulturist'' 2: 557–58)<ref>William W. Valk, “Design for a Geometric Flower Garden,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 2, no. 12 (June 1848): 557–59, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/VZ54DTTE view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| + | :“I send you a plan for a '''geometrical''' [[flower garden]]. It was designed by Mr. Brown, gardener to the late Duke of Buckingham, and is a very pretty thing of the kind. | ||
| + | :“When the nature of the ground will admit, the French [[parterre]], or '''geometrical''' [[flower garden]], is, above all others, the most to be recommended, for many situations, because it readily admits of the largest display of flowers throughout the season. There is scarcely any difficulty in producing a splendid show once or twice in the year, spring and autumn; and in consequence of many gentlemen not residing all the season near their [[flower garden]]s, the gardeners have an additional advantage in such places to produce, at the required time, the best display of flowers.” [Fig. 6] | ||
| − | + | *Elder, Walter, 1849, ''The Cottage Garden of America'' (1849: 26)<ref>Walter Elder, ''The Cottage Garden of America'' (Philadelphia: Moss, 1849), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/NNC7BTFT view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“If [the rich man’s [[lawn]] is constructed] in the '''geometrical style''', the trees will stand in lines or figures; some cut into different shapes and forms, from a [[seat]] to a [[temple]].” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Ranlett, William H., 1849, ''The Architect'' (1849; repr., 1976: 4)<ref>William H. Ranlett, ''The Architect'', 2 vols. (1849–51; repr., New York: Da Capo, 1976), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/QGQPCB5J view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| + | :“[[Landscape Gardening]] was, formerly, the imitation of '''geometric''' figures; hence the [[ancient style|ancient]] mode of it is called the '''geometric style''' of gardening.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], 1849, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849; repr., 1991: 21–22, 27, 91–93, 531)<ref>A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America'', 4th ed. (1849; repr., Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/K7BRCDC5 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“All late authors agree in these two distinct and widely different modes of the art; 1st, the [[ancient style|Ancient]], Formal, or '''Geometric Style'''; 2d, the [[Modern_style|Modern]], [[Natural style|Natural]], or Irregular Style. | |
| − | the | + | :“THE [[ANCIENT STYLE]]. A predominance of regular forms and right lines is the characteristic feature of the [[ancient style]] of gardening. The value of art, of power, and of wealth, were at once easily and strongly shown by an artificial arrangement of all the materials; an arrangement the more striking, as it differed most widely from nature. And in an age when costly and stately architecture was most abundant, as in the times of the Roman empire, it is natural to suppose, that the symmetry and studied elegance of the palace, or the villa, would be transferred and continued in the surrounding gardens. . . |
| − | + | :“Pliny’s garden, of which a pretty minute account remains,—filled with cypresses and bay trees, planted to form a coursing place or hippodrome, adorned with ''vis-à-vis'' figures of animals cut in box trees, and decorated with [[fountain]]s and marble [[alcove]]s, shaded by vines—seems, indeed, to have been the true classical type of all the later efforts of modern continental nations in their '''geometric''' gardens. . . | |
| − | + | [[File:0371.jpg|thumb|Fig. 7, Anonymous, Plantations in the Ancient Style, A Labyrinth, in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'' (1849), 91, fig. 17. ]] | |
| − | + | :“It would appear to be an undeniable fact in the history of ornamental gardening that, from the time of William the Conqueror down to the latter part of the reign of Queen Anne, and the beginning of that of George I., nothing was considered garden scenery except [if] it was in the formal and ''geometric style''. . . | |
| − | + | :“One of the favorite fancies of the '''geometric''' gardener was the [[Labyrinth]]. . . of which a few celebrated examples are still in existence in England, and which consisted of a multitude of trees thickly planted in impervious [[hedge]]s, covering sometimes several acres of ground. . . [Fig. 7] | |
| − | + | :“It has been remarked, that the '''geometric style''' would always be preferred in a new country, or in any country where the amount of land under cultivation is much less than that covered with natural [[wood]]s and forests; as the inhabitants being surrounded by scenery abounding with natural beauty, would always incline to lay out their gardens and [[pleasure-ground]]s in regular forms, because the distinct exhibition of art would give more pleasure by contrast, than the elegant imitation of beautiful nature. That this is true as regards the mass of uncultivated minds, we do not deny. But at the same time we affirm that it evinces a meagre taste, and a lower state of the art, or a lower perception of beauty in the individual who employs the '''geometrical style''' in such cases. . . : | |
| − | + | :“The only situation where this brilliant [white] gravel seems to us perfectly in keeping, is in the highly artificial garden of the [[Ancient_style|ancient]] or '''geometric style''', or in the symmetrical [[terrace]] [[flower garden]] adjoining the house. In these instances its striking appearance is in excellent keeping with the expression of all the surrounding objects, and it renders more forcible and striking the highly artificial and artistical character of the scene; and to such situations we would gladly see its use limited.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | and | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Images== | |
| − | + | ===Inscribed=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1753.jpg|[[J. C. Loudon]], “A Villa Residence of Two Acres, within a regular Boundary, laid out in the '''Geometrical''' Style,” in ''The Suburban Gardener'' (1838), 530, fig. 200. | |
| − | of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0997.jpg|Anonymous, “Design for a '''Geometric''' [[Flower Garden]],” in [[A. J. Downing]], ed., ''Horticulturist'' 2, no. 12 (June 1848): 558, fig. 67. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0370.jpg|Anonymous, “The '''Geometric''' style, from an old print,” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 62, fig. 14. | |
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Associated=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1675.jpg|Anonymous, Vignette of contrasting garden styles, in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 17. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | and | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0371.jpg|Anonymous, [[Plantation]]s in the [[Ancient style|Ancient Style]], A [[Labyrinth]], in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 91, fig. 17. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | ===Attributed=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | + | File:0017.jpg|Anonymous, Illustration of Williamsburg buildings, flora and fauna. Modern impression taken from the original 1740s copperplate [Bodleian Plate re-strike]. | |
| − | of | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0078.jpg|Anonymous, Plan for a garden, mid-18th century. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0248.jpg|Claude Joseph Sauthier, ''A Plan of the Town of Newbern in Craven County, North Carolina'', 1769. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:2159.jpg|Unknown, ''Bay, Elihu Hall, Plan Showing 1 Town Lot on Meeting Street in Charleston'', August 1789. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:2207.jpg|Alexander Jackson Davis, ''[United States Capitol, Washington D.C. East front elevation, rendering]'', [1834]. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0555a_detail2.jpg|Anonymous, [[Plat]] of 117 Broad Street [detail], 1797 . Register Mesne Conveyance, Charleston County, S.C. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0555a.jpg|Anonymous, [[Plat]] of 117 Broad Street, 1797. Register Mesne Conveyance, Charleston County, S.C. | |
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | < | ||
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references></references> | <references></references> | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Category: Keywords]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Garden Styles]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Styles]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:57, March 16, 2021
See also: Ancient style
History

The term geometric style came into use only when it was necessary to make a distinction between the traditional mode of laying out gardens and the newer modern, natural, or irregular style. Geometric, ancient, and formal were terms used interchangeably to describe gardens laid out symmetrically in straight lines, with strong axial circulation paths and geometrically regular beds [Fig. 1] (see Ancient style). The style was associated with French, Anglo-Dutch, and Italian traditions of gardening (see Dutch style and French style). In America, the geometric style continued to be popular long after the natural or modern style was introduced. As part of a larger landscaped garden, the flower garden was a feature that lent itself to regular shapes. Early public buildings such as the Governor’s Palace in Williamsburg, Virginia [Fig. 2], and Governor’s House in New Bern, North Carolina [Fig. 3], were laid out in a geometric style although, again, the term was used only after the modern style had become popular. The geometric style continued to be used in public places because of its long-standing association with centers of government.

The geometric style was also used well into the 19th century for domestic landscapes throughout the colonies. Often found in town gardens, this style suited the orthogonal layout of street plans and small lots.[1] It was equally prevalent in the plantation landscape throughout the South [Fig. 4].[2]
A. J. Downing’s description of Lemon Hill in Philadelphia explained the symmetry, uniformity, and high art of the geometric mode, listing the standard features of the style with its artificial plantations and highly regularized gardens. A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849) contains a miniature vignette of the two main modes of garden design [Fig. 4]. Downing’s descriptions of earlier American gardens, such as Lemon Hill, were respectful from a historical point of view. However, he denigrated his compatriots who continued to practice this mode. His English contemporary, Jane Loudon, whose work he was the first to publish in this country, described the geometric style succinctly without the negative tone found in garden writings such as Downing’s. Mrs. Loudon offered the style as an alternative, suitable and appropriate wherever symmetrical architecture existed. The term “artificial” was often used synonymously with “geometric,” especially when opposed to the so-called natural (or modern style), as in the quotations of George Watterston and Downing.
—Therese O’Malley
Texts
Usage
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, January 1837, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States” (Magazine of Horticulture 3: 8)[3]
- “The finest single example of landscape gardening, in the modern style, is at Dr. Hosack’s seat, Hyde Park, and the best specimens of the ancient or geometric style may probably be met with in the neighborhood of Philadelphia.”
- W., February 1842, describing Lowell Cemetery, Lowell, MA (Magazine of Horticulture 8: 49)[4]
- “In laying out these grounds, the skill of the designer has been displayed, in combining somewhat the ‘ancient or geometric style’ with the natural or irregular. In some parts, the regular forms and right lines are well adapted to the location of the ground, while in others, the varied and gradually curving forms give an air of grandeur and boldness, and in combining these with the natural scenery, cannot fail to call forth, in the minds of visitors, impressions of love and veneration.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, 1849, describing Lemon Hill, estate of Henry Pratt, Philadelphia (1849; repr., 1991: 43)[5]
- “Lemon Hill, half a mile above the Fairmount waterworks of Philadelphia, was, 20 years ago, the most perfect specimen of the geometric mode in America, and since its destruction by the extension of the city, a few years since, there is nothing comparable with it, in that style, among us. All the symmetry, uniformity, and high art of the old school, were displayed here in artificial plantations, formal gardens with trellises, grottoes, spring-houses, temples, statues, and vases, with numerous ponds of water, jets-d’eau, and other water-works, parterres and an extensive range of hothouses. The effect of this garden was brilliant and striking; its position, on the lovely banks of the Schuylkill, admirable; and its liberal proprietor, Mr. Pratt, by opening it freely to the public, greatly increased the popular taste in the neighborhood of that city.”
Citations
- Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius), 1826, An Encyclopaedia of Gardening (1826: 1005–6, 1020–21)[6]
- “7205. In planting in the geometric style, the first consideration is the nature of the whole or general design; and here, as in the ground, geometric forms will still prevail, and while the masses reflect forms from the house, or represent squares, triangles, or trapeziums, the more minute parts, characterised by lines rather than forms, such as avenues, rows, clumps, and stars, &c. are contained in parallelograms, squares, or circles. In regard to the parts, masses and avenues should extend from the house in all directions, so far as to diffuse around the character of design; and as much farther in particular directions as the nature of the surface admits of, the distant beauties suggest, and the character of the mansion requires. In disposing these masses, whether on a flat or irregular surface, regard will be had to leave uncovered such a quantity of lawn or turf as shall, at all events, admit a free circulation of air, give breadth of light, and display the form of the large masses of wood. Uniformity and variety as a whole, and use as well as beauty in the parts, must be kept constantly in view. Avenues, alleys, and vistas, should serve as much as possible as roads, walks, lines of fences, or screens of shelter or shade; but where this is not the case, they should point to some distant beauties, or near artificial objects, to be seen at or beyond their termination. The outer extremities of artificial plantations may either join natural woods, other artificial scenes, cultivated lands, or barren heaths or commons. . .
- “7262. The lawn, or that breadth of mown turf formed in front of, or extending in different directions from, the garden-front of the house, is, in the geometric style, varied by architectural forms, levels, and slopes; and in the modern by a picturesque or painter-like disposition of groups, placed so as to connect with the leading masses, and throw the lawn into an agreeable shape or shapes. In very small villas the lawn may embrace the garden or principal front of the house, without the intervention of terrace-scenery, and may be separated from the park, or park-like field, by a light wire fence; but in more extensive scenes it should embrace a terrace, or some avowedly artificial architectural basis to the mansion, and a sunk wall, as a distant separation, will be more dignified and permanent than any iron fence. The park may come close up to the terrace-garden, especially in a flat situation, or where the breadth of the terrace is considerable. . .
- “7265. The park. . . In the geometric style, the more distant or concealed parts were subdivided into fields, surrounded by broad stripes or double rows, enclosed in walls or hedges, and the nearer parts were chiefly covered with wood, enclosing regular surfaces of pasturage.”
- Anonymous, April 1, 1837, “Landscape Gardening” (Horticultural Register 3: 124)[7]
- “The uniformity produced by straight walks and alleys bordered by regular rows of trees, another characteristic of the old or geometrical style, though pleasing at first, soon becomes tiresome.”

- Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius), 1838, The Suburban Gardener (1838: 529–31)[8]
- “A Villa Residence of Two Acres, within a regular Boundary, laid out in the Geometrical Style.—The object in this case is to produce a splendid effect at a moderate expense of annual keeping, but with no regard to profit. The general form of the ground is that of a parallelogram, and its disposition is so clearly shown in the isometrical view. . . that it will require little or no description. The entrance is through a straight avenue to a flight of steps, which leads to a raised platform on which the house stands. To the right and left of the avenue are double rows of trees, which may be fruit-bearing kinds, such as the apple, pear, cherry, and plum. Beyond these, on each side, are two small kitchen-gardens, intended for gooseberries, strawberries, and other small fruits, and for pot-herbs, tart rhubarb, spinach, kidneybeans, and a few such vegetables as are desirable to have always at hand. The house and these kitchen-gardens occupy about half the entire residence.The other half is laid out in the form of a sunk flower-garden, consisting of a variety of curvilinear beds, bordered by a kerb of stone, and surrounded by turf. From the terrace walks there are four descents to this garden, each consisting of a double flight of steps. Each bed is supposed to be planted with one kind of herbaceous plant, so as to produce large masses of colour. The mode of selecting plants for this purpose, as well as lists of suitable plants, have been already given (p. 217 to p. 226), and further resources will be found in our catalogue. The sloping border between the sunk area and the flower-garden may either be planted with low evergreen shrubs, with roses kept low, or it may be in turf, or in rockwork: in the latter case, it may be covered with a collection of rock plants. Perhaps the most appropriate disposition of this sloping border would be to vary it with ornaments of box, on a ground of turf, so as to give it the appearance of an architectural moulding. In the centre there is a fountain. In situations where so much turf was not desirable, the walks between the beds might be of gravel or paved; but they will produce the best effect in turf.” [Fig. 5]
- W., M. A., February 1840, “On Flower Beds” (Magazine of Horticulture 6: 52)[9]
- “It is probably as difficult to fix upon the most suitable plant for the edging of a flower bed, as it is to determine the best shrub for a hedge around fields. For the borders of main avenues, or broad walks in grounds of considerable extent, box, as recommended, Vol. V., p. 350, is undoubtedly the best; but for small parterres, or the flower beds in a front door yard, it seems much less suitable. They can commonly be taken in at one glance of the eye, and notwithstanding all that has been said of the artificial or geometric style, it is the proper one for such places; for symmetry, or a perfect balance of corresponding parts, greatly strengthens the impression of such a scene, taken as a whole, or single mass of objects. The beds, therefore, will not only be small, but when there is the proper variety in the form of them, some, at least, must have quite acute angles. Box, if thrifty, (and, sickly, it would be an eyesore any where,) soon takes up too much space in breadth.”
- Watterston, George, May 1844, “Landscape Gardening” (1844: 307–8, 310–11)[10]
- “The Dutch style, introduced by William III., and which prevailed in England for about fifty years was not much better, and was distinguished for sloped terraces formed of grass, land and water made into regular shapes by art, and adorned with trees in pots, or ‘planted alternately and clipped to preserve the most perfect regularity of shape’— and leisure, ‘in trim gardens, took his pleasure.’ ‘The compass and the square,’ says Walpole, ‘were of more use than the nurseryman. The measured walk, the quincunx and the étoile imposed their unsatisfying sameness on every royal and noble garden. Trees were headed and their sides pared away; many French groves seem green chests set upon poles. Seats of marble, arbors and summer houses terminated every vista, and symmetry, even when the space was too large to permit its being remarked at one view, was so essential, that, as Pope observed,
- This formal, or geometric style was all the rage at the commencement of the 17th century in those parts of Europe where ornamental gardening prevailed, and the most distinguished artist of that age, if artist he could be called, was Le Notre. . .
- “In passing from the ancient, or geometric style, to the modern, or natural, the first improvers fell, perhaps, into an opposite extreme. This is the danger in all sudden transitions. They seemed to conceive that crooked lines, serpentine windings and carelessness were true objects of beauty, and declared that nature abhorred a straight line; and thus fatigued the eye by incessant curves. They did not seem to be aware, that in her sublimest works nature prefers the straight line, as is shown in the apparent horizon of the ocean and the rays of the sun.”
- Loudon, Jane, 1845, Gardening for Ladies (1845: 221–22)[11]
- “GEOMETRIC GARDENS.—This style of gardening is that in which the shape of the ground, of the beds, of the walks, and even of the shrubs, is regular, or symmetrical; such as may be formed on paper by a rule and compass. The ground, if originally flat, is reduced to a general level surface, over which the beds, or borders, are distributed so as to form figures, either simply regular, such as squares and parallelograms, repeated one after another—or squares and parallelograms, and circles or ovals, or other curvilinear figures,—so arranged as to be symmetrical; that is to say, that one-half of the figure formed by the whole shall correspond with the other half. When the surface is naturally irregular or on a slope, it is thrown into different levels, which are joined by steep slopes called terraces, generally covered with turf, and ascended and descended by stone steps. Each of the levels is laid out either regularly or symmetrically, in the same manner as if the whole were only one bed; but the figures are of course smaller. Small trees or evergreen shrubs are distributed among the figures, and especially on each side of the main walks; and these trees or shrubs ought, in strict accordance with the style, to be cut or clipped into regular shapes; such as cones, pyramids, balls, candelabra, statues of men or animals, arcades, columns, or other architectural figures. In modern practice, this is generally neglected; but its omission is a defect, for cut trees are as essential to the geometric style, as having the ground cut or shaped into artificial surfaces.”
- Thomas, John J., April 1848, “The Shrubbery and Flower Garden” (Cultivator 5: 114)[12]
- “Nearly all the flower gardens of the country are laid out in geometrical lines; a style, it is true much better adapted to the small piece of ground allotted to flowers, than to the larger landscape garden composed of trees, lawns, and sheets of water. With a wish however, to encourage a more graceful, pleasing, and picturesque mode of laying out even the small flower garden in connexion with the shrubbery, we have given the above plan, which nearly explains itself.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, May 1848, “Design for a Small Flower Garden” (Horticulturist 2: 503)[13]
- “The old geometric flower gardens, laid out with long beds, bordered with box, and separated by stiff gravel walks, are fast giving place to those more tasteful combinations of masses of gay, perpetual flowering plants, arranged upon turf, in the arabesque or English style.
- “In the former, you have a miscellaneous collection of plants, of all sizes and habits of growth, only a small part of which are seen in bloom at one time; while at almost all seasons naked stalks of plants, and bare dry soil borders, appear here and there, almost in spite of the best efforts of the gardener, to disfigure and mar the general elegance of the scene.
- “In the latter, you have always the rich setting of the soft green turf, (which, of course mown once a fortnight, is short and velvet-like) and contrasting and enhanced in effect by this, are seen the beds of dwarfish plants, grown in masses, so as to give breadth and brilliancy of effect; these being composed only of plants almost perpetually in bloom, unite to form a floral picture, when well managed, as beautiful as the art of gardening will permit.”

- Valk, Dr. William W., June 1848, “Design for a Geometric Flower Garden” (Horticulturist 2: 557–58)[14]
- “I send you a plan for a geometrical flower garden. It was designed by Mr. Brown, gardener to the late Duke of Buckingham, and is a very pretty thing of the kind.
- “When the nature of the ground will admit, the French parterre, or geometrical flower garden, is, above all others, the most to be recommended, for many situations, because it readily admits of the largest display of flowers throughout the season. There is scarcely any difficulty in producing a splendid show once or twice in the year, spring and autumn; and in consequence of many gentlemen not residing all the season near their flower gardens, the gardeners have an additional advantage in such places to produce, at the required time, the best display of flowers.” [Fig. 6]
- Elder, Walter, 1849, The Cottage Garden of America (1849: 26)[15]
- “If [the rich man’s lawn is constructed] in the geometrical style, the trees will stand in lines or figures; some cut into different shapes and forms, from a seat to a temple.”
- Ranlett, William H., 1849, The Architect (1849; repr., 1976: 4)[16]
- “Landscape Gardening was, formerly, the imitation of geometric figures; hence the ancient mode of it is called the geometric style of gardening.”
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, 1849, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening (1849; repr., 1991: 21–22, 27, 91–93, 531)[17]
- “All late authors agree in these two distinct and widely different modes of the art; 1st, the Ancient, Formal, or Geometric Style; 2d, the Modern, Natural, or Irregular Style.
- “THE ANCIENT STYLE. A predominance of regular forms and right lines is the characteristic feature of the ancient style of gardening. The value of art, of power, and of wealth, were at once easily and strongly shown by an artificial arrangement of all the materials; an arrangement the more striking, as it differed most widely from nature. And in an age when costly and stately architecture was most abundant, as in the times of the Roman empire, it is natural to suppose, that the symmetry and studied elegance of the palace, or the villa, would be transferred and continued in the surrounding gardens. . .
- “Pliny’s garden, of which a pretty minute account remains,—filled with cypresses and bay trees, planted to form a coursing place or hippodrome, adorned with vis-à-vis figures of animals cut in box trees, and decorated with fountains and marble alcoves, shaded by vines—seems, indeed, to have been the true classical type of all the later efforts of modern continental nations in their geometric gardens. . .
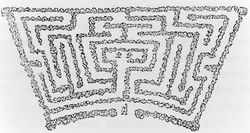
- “It would appear to be an undeniable fact in the history of ornamental gardening that, from the time of William the Conqueror down to the latter part of the reign of Queen Anne, and the beginning of that of George I., nothing was considered garden scenery except [if] it was in the formal and geometric style. . .
- “One of the favorite fancies of the geometric gardener was the Labyrinth. . . of which a few celebrated examples are still in existence in England, and which consisted of a multitude of trees thickly planted in impervious hedges, covering sometimes several acres of ground. . . [Fig. 7]
- “It has been remarked, that the geometric style would always be preferred in a new country, or in any country where the amount of land under cultivation is much less than that covered with natural woods and forests; as the inhabitants being surrounded by scenery abounding with natural beauty, would always incline to lay out their gardens and pleasure-grounds in regular forms, because the distinct exhibition of art would give more pleasure by contrast, than the elegant imitation of beautiful nature. That this is true as regards the mass of uncultivated minds, we do not deny. But at the same time we affirm that it evinces a meagre taste, and a lower state of the art, or a lower perception of beauty in the individual who employs the geometrical style in such cases. . . :
- “The only situation where this brilliant [white] gravel seems to us perfectly in keeping, is in the highly artificial garden of the ancient or geometric style, or in the symmetrical terrace flower garden adjoining the house. In these instances its striking appearance is in excellent keeping with the expression of all the surrounding objects, and it renders more forcible and striking the highly artificial and artistical character of the scene; and to such situations we would gladly see its use limited.”
Images
Inscribed
J. C. Loudon, “A Villa Residence of Two Acres, within a regular Boundary, laid out in the Geometrical Style,” in The Suburban Gardener (1838), 530, fig. 200.
Anonymous, “Design for a Geometric Flower Garden,” in A. J. Downing, ed., Horticulturist 2, no. 12 (June 1848): 558, fig. 67.
Anonymous, “The Geometric style, from an old print,” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, 4th ed. (1849), 62, fig. 14.
Associated
Anonymous, Vignette of contrasting garden styles, in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, 4th ed. (1849), 17.
Anonymous, Plantations in the Ancient Style, A Labyrinth, in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, 4th ed. (1849), 91, fig. 17.
Attributed
Anonymous, Plat of 117 Broad Street [detail], 1797 . Register Mesne Conveyance, Charleston County, S.C.
Anonymous, Plat of 117 Broad Street, 1797. Register Mesne Conveyance, Charleston County, S.C.
Notes
- ↑ For a discussion of geometric layouts of Louisiana gardens, see Suzanne Turner, “Roots of a Regional Garden Tradition: The Drawings of the New Orleans Notarial Archives,” in Regional Garden Design in the United States, ed. T. O’Malley and M. Treib (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1995), 163–90, view on Zotero.
- ↑ For a discussion of the geometrical principles of plantation layouts, see C. Allan Brown, “Eighteenth-Century Virginia Plantation Gardens: Translating an Ancient Idyll,” in Regional Garden Design in the United States, 125–62, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Andrew Jackson Downing, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States,” Magazine of Horticulture 3 (1837): 1–10, view on Zotero.
- ↑ W., “An Account of the Lowell Cemetery, Its Situation, Historical Associations, and Particular Description,” Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs 8 (1842): 47–50, view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America, 4th ed. (Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), view on Zotero.
- ↑ J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, An Encyclopaedia of Gardening; Comprising the Theory and Practice of Horticulture, Floriculture, Arboriculture, and Landscape-Gardening, 4th ed. (London: Longman et al., 1826), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Anonymous, “Landscape Gardening,” Horticultural Register and Gardener’s Magazine 3 (April 1837): 121–31, view on Zotero.
- ↑ J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, The Suburban Gardener, and Villa Companion (London: Longman et al., 1838), view on Zotero.
- ↑ M. A. W., “On Flower Beds,” Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs 6 (February 1840): 51–54, view on Zotero.
- ↑ George Watterston, “Landscape Gardening,” Southern Literary Messenger 10 (May 1844): 306–15, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Jane Loudon, Gardening for Ladies; and Companion to the Flower-Garden, ed. A. J. Downing (New York: Wiley & Putnam, 1845), view on Zotero.
- ↑ John J. Thomas, “The Shrubbery and Flower Garden,” Cultivator, a Monthly Publication, Devoted to Agriculture 5, no. 4 (April 1848): 114–16, view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. Downing, “Design for a Suburban Garden,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 3 (May 1848): 380, view on Zotero.
- ↑ William W. Valk, “Design for a Geometric Flower Garden,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 2, no. 12 (June 1848): 557–59, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Walter Elder, The Cottage Garden of America (Philadelphia: Moss, 1849), view on Zotero.
- ↑ William H. Ranlett, The Architect, 2 vols. (1849–51; repr., New York: Da Capo, 1976), view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America, 4th ed. (1849; repr., Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), view on Zotero.