Difference between revisions of "Jet"
V-Federici (talk | contribs) m (→Inscribed) |
|||
| (70 intermediate revisions by 9 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | (Jet | + | (''Jet d’eau'', Jet of water) {{break}} |
| − | See also: [[Basin | + | See also: [[Basin]], [[Fountain]], [[Lake]] |
==History== | ==History== | ||
| + | [[File:0044.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 1, [[Charles Willson Peale]], ''[[View]] of the garden at [[Belfield]]'', 1816.]] | ||
| + | The term jet (used both in its French form ''jet d’eau'' and its English translation “jet of water”) was used to describe a [[fountain]] consisting of a single continuous stream of water that was discharged into the air. The scale of jets ranged from modest, like the 10-foot example at [[Belfield]] [Fig. 1], to the spectacular, such as the jet of 30 or 40 feet that would water surrounding gardens proposed for the [[Columbian Institute]] in Washington, DC. | ||
| − | + | [[File:0538.jpg|thumb|left|Fig. 2, W. H. Bartlett (artist), J. Giles (engraver), ''Fairmount Gardens, with the Schuylkill Bridge'', 1839.]] | |
| + | [[File:0460.jpg|thumb|Fig. 3, Charles Varlé, ''Project for the Improvement of the Square and the Town of Bath'', 1809. “C. Jet d’eau.”]] | ||
| + | The height of the jet was a function of the [[fountain|fountain's]] aperture and available water pressure. Before the advent of city pressurized water systems, these specifications or dimensions were generally determined by the diameter of the pipe and by the elevation of the reservoir, cistern, spring, or other water source. Peale’s design for [[Belfield]] added a gilded ball supported by the jet, which reduced its height by half (see [[Fountain]]). The advantage of a single jet was that it was relatively simple to construct, it conserved water, and it could issue a higher spout than a [[fountain]] with multiple streams, such as a “tazza” (or weeping) [[fountain]]. The scale of the jet made this type of [[fountain]] particularly appropriate for large-scale gardens, such as Capitol Square in Richmond, Virginia, or Fairmount Waterworks in Philadelphia [Fig. 2], where the visibility of a tall jet from a distance created a dramatic effect. The effect of a single jet was also admired in the middle of a still-water basin or pool, as at [[Belfield]] or in Charles Varlé’s design for the town of Bath (Berkeley Springs), Virginia (later West Virginia), where he planned a ''jet d’eau'' in the center of a rectangular “[[bason]]” [Fig. 3]. In these examples the aesthetic appeal of the jet stemmed from the contrast of the vertical spout with the horizontal plane of the pool and the play of the spray on the surface of the water. The simplicity was, as [[Andrew_Jackson_Downing|Downing]] noted, also suited to sylvan scenes where other more elaborate [[fountain]]s would be considered too artificial. Even though concepts of garden hydraulic technology were widely published by the early 18th century,<ref>Stephen Switzer, ''An Introduction to a General System of Hydrostaticks and Hydraulicks, Philosophical and Practical'' (London: Printed for T. Astley, S. Austen, and L. Gilliver, 1729; repr., New York: Garland, 1982), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/4JXBZ2FU view on Zotero]. Our research has not found any evidence that this work was prevalent in the colonies. More widely available treatises, which are cited in the term record (such as Miller and Chambers), discuss the role of fountains in garden design, but they do not include the detailed technical information that is found in Switzer.</ref> the making of jets of water and other [[fountain]]s was expensive and not common in American gardens until the early 19th century. | ||
| − | + | —''Elizabeth Kryder-Reid'' | |
| − | + | <hr> | |
==Texts== | ==Texts== | ||
| − | |||
===Usage=== | ===Usage=== | ||
| + | *Peale, Rubens, September 27, 1813, in a letter to Sybilla Miriam Peale Summers, describing [[Belfield]], estate of [[Charles Willson Peale]], Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 1991: 3:206)<ref name="Miller et al">Lillian B. Miller et al., eds., ''The Selected Papers of Charles Willson Peale and His Family'', vol. 3, ''The Belfield Farm Years, 1810–1820'' (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1991), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/IZAKPCBG view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“Franklin has finished the [[Fountain]], it is a very handsome thing and gives very general pleasure. the '''get''' ['''jet'''] is about 10 feet in height from the surface of the [[Pond]], a Gilt Ball is thrown about 5 high and there suspinded [''sic''] by the force of the Water. Spiral [[fountain]] Triaes &c.” [See Fig. 1] | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Peale, Charles Willson]], March 15, 27, 29, 1814, in a letter to his sons, Benjamin Franklin Peale and Titian Ramsey Peale, describing [[Belfield]], estate of [[Charles Willson Peale]], Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 1991: 3:239)<ref name="Miller et al"></ref> | |
| − | + | :“. . . when my leasure and I can spare a man to hall dirt I will raise the water in the fish [[Pond]] which will encrease its surfaces considerably raising the water to the stone [[wall]] at the head of the [[Pond]], deeper, and more water, will be better for fish & will raise the '''get''' ['''jet'''] at the [[fountain]] considerably.” [See Fig. 1] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Peale, Charles Willson]], c. 1825, describing [[Belfield]], estate of [[Charles Willson Peale]], Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 2000: 5:383)<ref>Lillian B. Miller et al., eds., ''The Selected Papers of Charles Willson Peale and His Family'', vol. 5, ''The Autobiography of Charles Willson Peale'' (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2000), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/IZAKPCBG view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“. . . below the [[Green house]] he made a round [[bason]] to receive the Water from the cave back of it—and from the fish-[[pond]] near the spring-house, to this [[basin|bason]] in the Garden is a fall of 15 feet, and in order to have a [[fountain]] in the [[basin|Bason]] he put log-pipes under ground, and thus had a '''jet''' of 13 feet high, but of small diameter, in order that it might constantly [be] rising. but unfortunately he make the bore of his logs only of one Inch diameter, the consequence was that Frogs in two instances got into the bore of the logs and not being able to pass through all the joints, stopped the water, of course to free the passage of the logs, gave much labour. had these things been foreseen, trouble might have been prevented, by making the bore of the logs of a greater diameter, with other provisions to keep the passage free.” [See Fig. 1] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Hunt, Henry, William P. Elliot, and William Thornton, 1826, describing the [[national Mall]], Washington, DC (U.S. Congress, 19th Congress, 1st Session, House of Representatives, doc. 123, book 138) | |
| − | + | :“That, with a [[view]] to promote the public good, and to ornament and improve the [[public ground]]s, they would recommend that the water of Tiber Creek be brought to the Capitol Square; and, after forming a reservoir, be carried in pipes to the [[Botanic Garden]], and thrown up in a '''jet d’eau''' of 30 or 40 feet high, and then be used in watering the surrounding grounds.” | |
| − | |||
| − | in | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:0536.jpg|thumb|Fig. 4, George Lehman, ''Fairmount Waterworks. From the Forebay'', 1833.]] | |
| − | + | *Trollope, Frances Milton, 1830, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (1832: 2:42, 44)<ref>Frances Milton Trollope, ''Domestic Manners of the Americans'', 2 vols. (London: Wittaker, Treacher & Co., 1832), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/MBMCV4N6 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“The water-works of Philadelphia have not yet perhaps as wide extended fame as those of Marley, but they are not less deserving it. . . | |
| − | + | :“At another point, a portion of the water in its upward way to the reservoir, is permitted to spring forth in a perpetual '''''jet d’eau''''', that returns in a silver shower upon the head of a marble naïad of snowy whiteness.” [Fig. 4] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | of the | ||
| − | to | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], January 1837, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States,” describing [[Lemon Hill]], estate of [[Henry Pratt]], Philadelphia, PA (''Magazine of Horticulture'' 3: 4)<ref>Andrew Jackson Downing, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States”, ''Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs'' 3, no. 1 (January 1837): 1–10, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/HPNHTESI view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“For a long time the grounds of [[Henry Pratt|Mr. Pratt]], at [[Lemon Hill]], near Philadelphia, have been considered the show-garden of that city: and the proprietor, with a praiseworthy spirit, opening his long-shaded [[walk]]s, cool [[grotto]]es, '''jets d’eau''', and the superb range of [[hot-house]]s, to the inspection of the citizens, contributed in a wonderful degree to improve the taste of the inhabitants, and to inspire them with a desire to possess the more beautiful and delicate productions of nature.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Bryant, William Cullen, July 3, 1844, describing in an editorial in the ''New York Evening Post'' Jones Wood, estate of John Jones, New York, NY (quoted in Rosenzweig and Blackmar 1992: 21)<ref>Roy Rosenzweig and Elizabeth Blackmar, ''The Park and the People: A History of Central Park'' (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1992), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/GFRVMGF9 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“Nothing is wanted [to transform the Jones Wood into a public [[park]]] but to cut winding paths through it, leaving the [[wood]]s as they now are, and introducing here and there a '''jet''' from the Croton aqueduct.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Committee on the Capitol Square, Richmond City Council, July 26, 1851, describing John Notman’s plans for the Capitol Square, Richmond, VA (quoted in Greiff 1979: 162)<ref>Constance Greiff, ''John Notman, Architect, 1810–1865'' (Philadelphia: Athenaeum of Philadelphia, 1979), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/SXT2RI6Z view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“. . . [[walk]]s will be made in every direction and as some compensation for filling up the beautiful vale south of the Monument a capacious [[fountain]] will be placed in the centre of the [[walk]] leading into Bank street, from which [[fountain]] a '''jet d’eau''' will rise, fully thirty feet in height. The eastern portion of the [[square]] will likewise undergo considerable change—the rugged features will be materially softened down, a [[fountain]] and '''jet d’eau''' to correspond with those on the western side will be placed in the valley near the state courthouse.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Watson, John, 1857, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (1857: 1:489)<ref>John Fanning Watson, ''Annals of Philadelphia and Pennsylvania in the Olden Time. . .'' 2 vols. (Philadelphia: E. Thomas, 1857), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/5PTKBUW2 view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“There we see the graceful, glittering river winding amongst its wooded banks, the artificial [[cascade]] at your feet, the lovely '''jet d’eaux''' all around, the green [[plat]]s and gravelled [[walk]]s through which you have walked, the [[picturesque]] [[view]]s wherever you cast your eyes, these go to make up the picture which is spread out in rich luxuriance before you.” | ||
===Citations=== | ===Citations=== | ||
| + | *[[Chambers, Ephraim]], 1741, ''Cyclopaedia'' (1741: 1:n.p.)<ref>Ephraim Chambers, ''Cyclopaedia, or An Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences. . . '', 5th edn, 2 vols (London: D. Midwinter et al., 1741–43), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/PTXK378N view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“AJUTAGE, or ADJUTAGE, in hydraulics, part of the apparatus of an artificial [[fountain]], or '''jet d’eau'''; being a sort of tube, fitted to the mouth or aperture of the vessel: through which the water is to be played, and by it determined into this or that figure. . . | ||
| + | :“[[FOUNTAIN]], or artificial [[FOUNTAIN]], in hydraulicks, a machine, or contrivance, whereby the water is violently spouted, or darted up; called also '''''Jet d’Eau''''' See '''''JET d’Eau''''', FLUID, ''&c''. . . | ||
| + | :“[[GROTTO]], is also used for a little artificial edifice made in a garden, in imitation of a natural [[grotto]]. | ||
| + | :“The outsides of these [[grotto]]’s are usually adorned with [[Rustic_style|rustic]] architecture, and their inside with shell-work, furnished like-wise with various '''jet d’eaus''', or [[fountain]]s, ''&c''. . . | ||
| + | :“'''JET D’EAU''', a French word, signifying a ''[[fountain]]'' that casts up water to any considerable heighth in the air. See [[FOUNTAIN]]. | ||
| + | :“Mariotte shews, that a '''''jet d’eau''''' will never raise water so high as its reservoir, but always falls short of it by a space, which is in a subduplicate ratio of that heighth.—The same author shews, that if a greater '''''jet''''' branch out into many smaller ones, or be distributed through several '''''jets''''', the square of the diameter of the main pipe, must be proportioned to the sum of all the expences of its branches: and that if the reservoir be 52 foot high, and the adjutage half an inch in diameter, the pipe ought to be three inches in diameter.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | (1:n.p.) | + | *Johnson, Samuel, 1755, ''A Dictionary of the English Language'' (1755: 1:n.p.)<ref>Samuel Johnson, ''A Dictionary of the English Language: In Which the Words Are Deduced from the Originals and Illustrated in the Different Significations by Examples from the Best Writers'', 2 vols. (London: W. Strahan for J. and P. Knapton, 1755), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/GE2JPJR3 view on Zotero].</ref> |
| + | :“'''JET'''. ''n.s''. [. . . Saxon; ''get'', Dutch; ''gagates'', Latin.] | ||
| + | :“2. ['''''Jet''''', French.] A spout or shoot of water.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Miller, Philip, 1759, ''The Gardeners Dictionary'' (1759; repr., 1969: n.p.)<ref>Philip Miller, ''The Gardeners Dictionary'' (1759; repr., New York: Verlag Von J. Cramer, 1969), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/356Q24EP view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“'''Jet d’eau''' is a French word, which signifies a [[fountain]] that casts up water to any consideration Height in the Air. These spouts of Water are some of the greatest Beauties of the Italian Gardens, and are certainly better adapted for Gardens in their warm countries, than they are for our climate, because in the great Heat of summer, the sight of these water spouts is cooling and refreshing to the Imagination, and they certainly add a real coolness to the Air, but in cold countries they cool the Air too much, therefore should not be erected; or if they are, they should be placed at such Distances from the Habitation, as that the Damp may no ways affect it. . . Where '''jets''' are contrived, if there is not a constant supply for a large column of water, they should by no means be made.” | |
| − | the water is | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Marshall, Charles, 1799, ''An Introduction to the Knowledge and Practice of Gardening'' (1799: 1:126)<ref>Charles Marshall, ''An Introduction to the Knowledge and Practice of Gardening'', 1st American ed., 2 vols. (Boston: Samuel Etheridge, 1799), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/DVB7T4I2 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“Every ''spring'' of water should be made the most of, and though ''[[fountain]]s '''jets d’eau''''': ''&c''. are out of fashion, something of this kind is agreeable enough.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *[[J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon|Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius)]], 1826, ''An Encyclopaedia of Gardening'' (1826: 358–59, 1009)<ref>J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, ''An Encyclopaedia of Gardening; Comprising the Theory and Practice of Horticulture, Floriculture, Arboriculture, and Landscape-Gardening'', 4th ed. (London: Longman et al., 1826), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/KNKTCA4W view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“1822. ''Of constructions for displaying water'', as an artificial decoration, the principal are [[cascade]]s, [[waterfall]]s, '''jets''', and [[fountain]]s. . . | |
| − | + | :“1829. '''''Jets''' and other hydraulic devices'', though now in less repute than formerly, are not to be rejected in confined artificial scenes, and form an essential decoration where the [[ancient style]] of landscape is introduced in any degree of perfection. | |
| − | + | :“1830. ''The first requisite for '''jets''' or projected spouts, or threads of water'', by atmospheric pressure, is a sufficiently elevated source or reservoir of supply. This being obtained, pipes are to be conducted from it to the situations for the '''jets'''. . . | |
| − | + | :“1831. ''Adjutages'' are of various sorts. Some are contrived so as to throw up the water in the form of sheaves, fans, showers, to support balls, &c.; others to throw it out horizontally, or in curved lines, according to the taste of the designer; but the most usual form is a simple opening to throw the spout or '''jet''' upright. The grandest '''jet''' of any is a perpendicular [[column]] issuing from a rocky base, on which the water falling, produces a double effect both of sound and visual display. A '''jet''' rising from a naked tube in the middle of a [[basin]] or [[canal]], and the waters falling on its smooth surface, is unnatural, without being artificially grand.” | |
| − | + | :"7216. ''Water'' is a material of so captivating and interesting a description in the different characters in which it does not compose a feature. It forms a part of every garden in the [[Ancient style|ancient style]] in the various artificial characters which it there assumes of oblong [[canal]]s, [[pond]]s, [[basin]]s, [[cascade]]s, and '''''jeux-d’eau''''' ''(fig. 694)'' ;" | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | and the | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | *Teschemacher, James E., August 1, 1835, “Extracts from Foreign Publications” (''Horticultural Register'' 1: 308–9)<ref>James E. Teschemacher, “Extracts from Foreign Publications,” ''Horticultural Register, and Gardener’s Magazine'' 1 (August 1, 1835): 304–9, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/CNPGMS5X/ view on Zotero].</ref> | ||
| + | :“From an article ''On the various form and character of [[Arbour]]s as objects of use or ornament either in gardens or wild scenery'' [from ''Paxton’s Horticultural Register''], we extract the following passages. . . | ||
| + | :“‘The interior is an [[arbor]] of great magnitude, not so closely covered as everywhere absolutely to exclude the sun, but yet so as to render is always shady and agreeable. In the centre a cooling [[fountain]], where a group of nymphs support the pole, sends forth four '''jets d’eau''', which drop with delicious murmurs into a marble [[basin]].’” | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Tuthill, Louisa C. (Louisa Caroline), 1848, ''History of Architecture'' (1848: 396)<ref>Louisa C. Tuthill, ''History of Architecture, from the Earliest Times; Its Present Condition in Europe and the United States. . . '', (Philadelphia: Lindsay and Blakiston, 1848), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/4ACTS7DK view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| + | :“'''''Jet d’eau'''''. Water thrown into the air from a pipe or tube, and falling into a [[basin]] below.” | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:0402.jpg|thumb|Fig. 5, Anonymous, “A simple jet,” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 471, fig. 92. “A simple jet. . . issuing from a circular basin of water. . .”]] | |
| + | *[[Andrew Jackson Downing|Downing, Andrew Jackson]], 1849, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Gardening'' (1849; repr., 1991:466, 471) <ref>A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America,'' 4th ed. (1849; repr., Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/K7BRCDC5 view on Zotero]. </ref> | ||
| + | :“''[[Fountain]]s'' are highly elegant garden decorations, rarely seen in this country; which is owing, not so much, we apprehend, to any great cost incurred in putting them up, or in any want of appreciation of their sparkling and enlivening effect in garden scenery, as to the fact that there are few artisans here, as abroad, whose business it is to construct and fit up architectural, and other '''''jets d’eau'''''. . . | ||
| + | :“A simple '''jet'''. . . issuing from a circular [[basin]] of water, or a cluster of perpendicular '''jets''' (candelabra '''jets'''), is at once the simplest and most pleasing of [[fountain]]s. Such are almost the only kinds of [[fountain]]s which can be introduced with propriety in simple scenes where the predominant objects are sylvan, not architectural.” [Fig. 5] | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | *Humphreys, Henry Noel, November 1850, “Notes on Decorative Gardening—Fountains” (''Horticulturist'' 5: 208)<ref>Henry Noel Humphreys, “Notes on Decorative Gardening-Fountains,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 5, no. 5 (November 1850): 208–11, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/items/itemKey/RF8S8ZNF view on Zotero]. </ref> | |
| − | fountain | + | :“But though we find natural [[fountain]]s in the wildest scenes of nature, it is not, however, necessary, in making artistic use of a natural law that produces a '''''jet d’eau''''', to surround the artificial '''jet''' with the circumstances that surround it in nature, any more than it is necessary that the architect, in building with stone, should imitate in his work the rude form of the quarry from which it was taken.” |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | *L., R. B., June 1851, “On Artificial Rockeries” (''Horticulturist'' 6: 279)<ref>R. B. L., “On Artificial Rockeries,” ''Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste'' 6, no. 6 (June 1851): 276–79, [https://www.zotero.org/groups/54737/keywords_in_early_american_landscape_design/items/itemKey/K4A8SS87 view on Zotero].</ref> | |
| − | + | :“It may likewise be observed that [[rockeries]] should always be in detached groups, and whether large or small, should never present straight lines or flat surfaces. The more irregular the arrangement, the more striking the effect produced. It should also be so situated as to be partly shaded and overhung by pendulous trees, to screen it from the glare of sunshine; it should always be rather cool, and if possible, shut in by itself by [[shrubbery]], and if possible, also, should be accompanied by a '''jet d’eau''' or [[basin]] of water, or both.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | <hr> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | ==Images== | |
| − | + | ===Inscribed=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0460.jpg|Charles Varlé, ''Project for the Improvement of the [[Square]] and the Town of Bath'', 1809. “C. Jet d’eau.” | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0402.jpg|Anonymous, "A simple '''jet'''. . . the simplest and most pleasing of [[fountain]]s” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 471, fig. 92. “A simple '''jet'''. . . issuing from a circular [[basin]] of water. . .” | |
| − | + | File:0403.jpg|Anonymous, “Tazza Fountain,” in [[A. J. Downing]], ''A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening'', 4th ed. (1849), 471, fig. 93. | |
| − | + | File:1597.jpg|Anonymous, “Natural '''Jet''' d’eau,” ''Horticulturist'' 5, no. 5 (November 1850): 208, fig. 55. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:2297.jpg|Matthew Vassar, ''Plan of Springside'', 1851. "'''Jet''' Vale Path (13)." | |
| − | + | </gallery> | |
| − | + | ===Associated=== | |
| − | + | <gallery widths="170px" heights="170px" perrow="7"> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0551.jpg|John Lewis Krimmel, ''Fourth of July in Centre [[Square]]'', 1812. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | in | ||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0044.jpg|[[Charles Willson Peale]], ''[[View]] of the garden at [[Belfield]]'', 1816. | |
| − | + | File:0044_detail3.jpg|[[Charles Willson Peale]], ''[[View]] of the garden at [[Belfield]]'', [detail] 1816. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:1368.jpg|[[J. C. Loudon]], A garden in the [[ancient style]], in ''An Encyclopædia of Gardening'' 4th ed. (1826), 1009, fig. 694. | |
| − | |||
| − | in | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0537.jpg|Tucker Factory, Pair of [[vase]]s with [[view]]s of the Fairmount Waterworks, c. 1830. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0536.jpg|George Lehman, ''Fairmount Waterworks. From the Forebay'', 1833. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | File:0538.jpg|W. H. Bartlett (artist), J. Giles (engraver), ''Fairmount Gardens, with the Schuylkill Bridge'', 1839. | |
| + | </gallery> | ||
| − | < | + | <hr> |
==Notes== | ==Notes== | ||
<references></references> | <references></references> | ||
| − | + | <hr> | |
[[Category: Keywords]] | [[Category: Keywords]] | ||
| + | [[Category: Water Features]] | ||
Latest revision as of 13:19, April 12, 2021
(Jet d’eau, Jet of water)
See also: Basin, Fountain, Lake
History
The term jet (used both in its French form jet d’eau and its English translation “jet of water”) was used to describe a fountain consisting of a single continuous stream of water that was discharged into the air. The scale of jets ranged from modest, like the 10-foot example at Belfield [Fig. 1], to the spectacular, such as the jet of 30 or 40 feet that would water surrounding gardens proposed for the Columbian Institute in Washington, DC.
The height of the jet was a function of the fountain's aperture and available water pressure. Before the advent of city pressurized water systems, these specifications or dimensions were generally determined by the diameter of the pipe and by the elevation of the reservoir, cistern, spring, or other water source. Peale’s design for Belfield added a gilded ball supported by the jet, which reduced its height by half (see Fountain). The advantage of a single jet was that it was relatively simple to construct, it conserved water, and it could issue a higher spout than a fountain with multiple streams, such as a “tazza” (or weeping) fountain. The scale of the jet made this type of fountain particularly appropriate for large-scale gardens, such as Capitol Square in Richmond, Virginia, or Fairmount Waterworks in Philadelphia [Fig. 2], where the visibility of a tall jet from a distance created a dramatic effect. The effect of a single jet was also admired in the middle of a still-water basin or pool, as at Belfield or in Charles Varlé’s design for the town of Bath (Berkeley Springs), Virginia (later West Virginia), where he planned a jet d’eau in the center of a rectangular “bason” [Fig. 3]. In these examples the aesthetic appeal of the jet stemmed from the contrast of the vertical spout with the horizontal plane of the pool and the play of the spray on the surface of the water. The simplicity was, as Downing noted, also suited to sylvan scenes where other more elaborate fountains would be considered too artificial. Even though concepts of garden hydraulic technology were widely published by the early 18th century,[1] the making of jets of water and other fountains was expensive and not common in American gardens until the early 19th century.
—Elizabeth Kryder-Reid
Texts
Usage
- Peale, Rubens, September 27, 1813, in a letter to Sybilla Miriam Peale Summers, describing Belfield, estate of Charles Willson Peale, Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 1991: 3:206)[2]
- “Franklin has finished the Fountain, it is a very handsome thing and gives very general pleasure. the get [jet] is about 10 feet in height from the surface of the Pond, a Gilt Ball is thrown about 5 high and there suspinded [sic] by the force of the Water. Spiral fountain Triaes &c.” [See Fig. 1]
- Peale, Charles Willson, March 15, 27, 29, 1814, in a letter to his sons, Benjamin Franklin Peale and Titian Ramsey Peale, describing Belfield, estate of Charles Willson Peale, Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 1991: 3:239)[2]
- “. . . when my leasure and I can spare a man to hall dirt I will raise the water in the fish Pond which will encrease its surfaces considerably raising the water to the stone wall at the head of the Pond, deeper, and more water, will be better for fish & will raise the get [jet] at the fountain considerably.” [See Fig. 1]
- Peale, Charles Willson, c. 1825, describing Belfield, estate of Charles Willson Peale, Germantown, PA (Miller et al., eds., 2000: 5:383)[3]
- “. . . below the Green house he made a round bason to receive the Water from the cave back of it—and from the fish-pond near the spring-house, to this bason in the Garden is a fall of 15 feet, and in order to have a fountain in the Bason he put log-pipes under ground, and thus had a jet of 13 feet high, but of small diameter, in order that it might constantly [be] rising. but unfortunately he make the bore of his logs only of one Inch diameter, the consequence was that Frogs in two instances got into the bore of the logs and not being able to pass through all the joints, stopped the water, of course to free the passage of the logs, gave much labour. had these things been foreseen, trouble might have been prevented, by making the bore of the logs of a greater diameter, with other provisions to keep the passage free.” [See Fig. 1]
- Hunt, Henry, William P. Elliot, and William Thornton, 1826, describing the national Mall, Washington, DC (U.S. Congress, 19th Congress, 1st Session, House of Representatives, doc. 123, book 138)
- “That, with a view to promote the public good, and to ornament and improve the public grounds, they would recommend that the water of Tiber Creek be brought to the Capitol Square; and, after forming a reservoir, be carried in pipes to the Botanic Garden, and thrown up in a jet d’eau of 30 or 40 feet high, and then be used in watering the surrounding grounds.”
- Trollope, Frances Milton, 1830, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (1832: 2:42, 44)[4]
- “The water-works of Philadelphia have not yet perhaps as wide extended fame as those of Marley, but they are not less deserving it. . .
- “At another point, a portion of the water in its upward way to the reservoir, is permitted to spring forth in a perpetual jet d’eau, that returns in a silver shower upon the head of a marble naïad of snowy whiteness.” [Fig. 4]
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, January 1837, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States,” describing Lemon Hill, estate of Henry Pratt, Philadelphia, PA (Magazine of Horticulture 3: 4)[5]
- “For a long time the grounds of Mr. Pratt, at Lemon Hill, near Philadelphia, have been considered the show-garden of that city: and the proprietor, with a praiseworthy spirit, opening his long-shaded walks, cool grottoes, jets d’eau, and the superb range of hot-houses, to the inspection of the citizens, contributed in a wonderful degree to improve the taste of the inhabitants, and to inspire them with a desire to possess the more beautiful and delicate productions of nature.”
- Bryant, William Cullen, July 3, 1844, describing in an editorial in the New York Evening Post Jones Wood, estate of John Jones, New York, NY (quoted in Rosenzweig and Blackmar 1992: 21)[6]
- “Nothing is wanted [to transform the Jones Wood into a public park] but to cut winding paths through it, leaving the woods as they now are, and introducing here and there a jet from the Croton aqueduct.”
- Committee on the Capitol Square, Richmond City Council, July 26, 1851, describing John Notman’s plans for the Capitol Square, Richmond, VA (quoted in Greiff 1979: 162)[7]
- “. . . walks will be made in every direction and as some compensation for filling up the beautiful vale south of the Monument a capacious fountain will be placed in the centre of the walk leading into Bank street, from which fountain a jet d’eau will rise, fully thirty feet in height. The eastern portion of the square will likewise undergo considerable change—the rugged features will be materially softened down, a fountain and jet d’eau to correspond with those on the western side will be placed in the valley near the state courthouse.”
- Watson, John, 1857, describing Fairmount Waterworks, Philadelphia, PA (1857: 1:489)[8]
- “There we see the graceful, glittering river winding amongst its wooded banks, the artificial cascade at your feet, the lovely jet d’eaux all around, the green plats and gravelled walks through which you have walked, the picturesque views wherever you cast your eyes, these go to make up the picture which is spread out in rich luxuriance before you.”
Citations
- Chambers, Ephraim, 1741, Cyclopaedia (1741: 1:n.p.)[9]
- “AJUTAGE, or ADJUTAGE, in hydraulics, part of the apparatus of an artificial fountain, or jet d’eau; being a sort of tube, fitted to the mouth or aperture of the vessel: through which the water is to be played, and by it determined into this or that figure. . .
- “FOUNTAIN, or artificial FOUNTAIN, in hydraulicks, a machine, or contrivance, whereby the water is violently spouted, or darted up; called also Jet d’Eau See JET d’Eau, FLUID, &c. . .
- “GROTTO, is also used for a little artificial edifice made in a garden, in imitation of a natural grotto.
- “The outsides of these grotto’s are usually adorned with rustic architecture, and their inside with shell-work, furnished like-wise with various jet d’eaus, or fountains, &c. . .
- “JET D’EAU, a French word, signifying a fountain that casts up water to any considerable heighth in the air. See FOUNTAIN.
- “Mariotte shews, that a jet d’eau will never raise water so high as its reservoir, but always falls short of it by a space, which is in a subduplicate ratio of that heighth.—The same author shews, that if a greater jet branch out into many smaller ones, or be distributed through several jets, the square of the diameter of the main pipe, must be proportioned to the sum of all the expences of its branches: and that if the reservoir be 52 foot high, and the adjutage half an inch in diameter, the pipe ought to be three inches in diameter.”
- Johnson, Samuel, 1755, A Dictionary of the English Language (1755: 1:n.p.)[10]
- “JET. n.s. [. . . Saxon; get, Dutch; gagates, Latin.]
- “2. [Jet, French.] A spout or shoot of water.”
- Miller, Philip, 1759, The Gardeners Dictionary (1759; repr., 1969: n.p.)[11]
- “Jet d’eau is a French word, which signifies a fountain that casts up water to any consideration Height in the Air. These spouts of Water are some of the greatest Beauties of the Italian Gardens, and are certainly better adapted for Gardens in their warm countries, than they are for our climate, because in the great Heat of summer, the sight of these water spouts is cooling and refreshing to the Imagination, and they certainly add a real coolness to the Air, but in cold countries they cool the Air too much, therefore should not be erected; or if they are, they should be placed at such Distances from the Habitation, as that the Damp may no ways affect it. . . Where jets are contrived, if there is not a constant supply for a large column of water, they should by no means be made.”
- Marshall, Charles, 1799, An Introduction to the Knowledge and Practice of Gardening (1799: 1:126)[12]
- “Every spring of water should be made the most of, and though fountains jets d’eau: &c. are out of fashion, something of this kind is agreeable enough.”
- Loudon, J. C. (John Claudius), 1826, An Encyclopaedia of Gardening (1826: 358–59, 1009)[13]
- “1822. Of constructions for displaying water, as an artificial decoration, the principal are cascades, waterfalls, jets, and fountains. . .
- “1829. Jets and other hydraulic devices, though now in less repute than formerly, are not to be rejected in confined artificial scenes, and form an essential decoration where the ancient style of landscape is introduced in any degree of perfection.
- “1830. The first requisite for jets or projected spouts, or threads of water, by atmospheric pressure, is a sufficiently elevated source or reservoir of supply. This being obtained, pipes are to be conducted from it to the situations for the jets. . .
- “1831. Adjutages are of various sorts. Some are contrived so as to throw up the water in the form of sheaves, fans, showers, to support balls, &c.; others to throw it out horizontally, or in curved lines, according to the taste of the designer; but the most usual form is a simple opening to throw the spout or jet upright. The grandest jet of any is a perpendicular column issuing from a rocky base, on which the water falling, produces a double effect both of sound and visual display. A jet rising from a naked tube in the middle of a basin or canal, and the waters falling on its smooth surface, is unnatural, without being artificially grand.”
- "7216. Water is a material of so captivating and interesting a description in the different characters in which it does not compose a feature. It forms a part of every garden in the ancient style in the various artificial characters which it there assumes of oblong canals, ponds, basins, cascades, and jeux-d’eau (fig. 694) ;"
- Teschemacher, James E., August 1, 1835, “Extracts from Foreign Publications” (Horticultural Register 1: 308–9)[14]
- “From an article On the various form and character of Arbours as objects of use or ornament either in gardens or wild scenery [from Paxton’s Horticultural Register], we extract the following passages. . .
- “‘The interior is an arbor of great magnitude, not so closely covered as everywhere absolutely to exclude the sun, but yet so as to render is always shady and agreeable. In the centre a cooling fountain, where a group of nymphs support the pole, sends forth four jets d’eau, which drop with delicious murmurs into a marble basin.’”
- Tuthill, Louisa C. (Louisa Caroline), 1848, History of Architecture (1848: 396)[15]
- “Jet d’eau. Water thrown into the air from a pipe or tube, and falling into a basin below.”
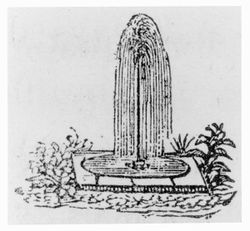
- Downing, Andrew Jackson, 1849, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Gardening (1849; repr., 1991:466, 471) [16]
- “Fountains are highly elegant garden decorations, rarely seen in this country; which is owing, not so much, we apprehend, to any great cost incurred in putting them up, or in any want of appreciation of their sparkling and enlivening effect in garden scenery, as to the fact that there are few artisans here, as abroad, whose business it is to construct and fit up architectural, and other jets d’eau. . .
- “A simple jet. . . issuing from a circular basin of water, or a cluster of perpendicular jets (candelabra jets), is at once the simplest and most pleasing of fountains. Such are almost the only kinds of fountains which can be introduced with propriety in simple scenes where the predominant objects are sylvan, not architectural.” [Fig. 5]
- Humphreys, Henry Noel, November 1850, “Notes on Decorative Gardening—Fountains” (Horticulturist 5: 208)[17]
- “But though we find natural fountains in the wildest scenes of nature, it is not, however, necessary, in making artistic use of a natural law that produces a jet d’eau, to surround the artificial jet with the circumstances that surround it in nature, any more than it is necessary that the architect, in building with stone, should imitate in his work the rude form of the quarry from which it was taken.”
- L., R. B., June 1851, “On Artificial Rockeries” (Horticulturist 6: 279)[18]
- “It may likewise be observed that rockeries should always be in detached groups, and whether large or small, should never present straight lines or flat surfaces. The more irregular the arrangement, the more striking the effect produced. It should also be so situated as to be partly shaded and overhung by pendulous trees, to screen it from the glare of sunshine; it should always be rather cool, and if possible, shut in by itself by shrubbery, and if possible, also, should be accompanied by a jet d’eau or basin of water, or both.”
Images
Inscribed
Charles Varlé, Project for the Improvement of the Square and the Town of Bath, 1809. “C. Jet d’eau.”
Anonymous, "A simple jet. . . the simplest and most pleasing of fountains” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, 4th ed. (1849), 471, fig. 92. “A simple jet. . . issuing from a circular basin of water. . .”
Anonymous, “Tazza Fountain,” in A. J. Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, 4th ed. (1849), 471, fig. 93.
Associated
John Lewis Krimmel, Fourth of July in Centre Square, 1812.
Charles Willson Peale, View of the garden at Belfield, 1816.
Charles Willson Peale, View of the garden at Belfield, [detail] 1816.
J. C. Loudon, A garden in the ancient style, in An Encyclopædia of Gardening 4th ed. (1826), 1009, fig. 694.
Notes
- ↑ Stephen Switzer, An Introduction to a General System of Hydrostaticks and Hydraulicks, Philosophical and Practical (London: Printed for T. Astley, S. Austen, and L. Gilliver, 1729; repr., New York: Garland, 1982), view on Zotero. Our research has not found any evidence that this work was prevalent in the colonies. More widely available treatises, which are cited in the term record (such as Miller and Chambers), discuss the role of fountains in garden design, but they do not include the detailed technical information that is found in Switzer.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Lillian B. Miller et al., eds., The Selected Papers of Charles Willson Peale and His Family, vol. 3, The Belfield Farm Years, 1810–1820 (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 1991), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Lillian B. Miller et al., eds., The Selected Papers of Charles Willson Peale and His Family, vol. 5, The Autobiography of Charles Willson Peale (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press, 2000), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Frances Milton Trollope, Domestic Manners of the Americans, 2 vols. (London: Wittaker, Treacher & Co., 1832), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Andrew Jackson Downing, “Notices on the State and Progress of Horticulture in the United States”, Magazine of Horticulture, Botany, and All Useful Discoveries and Improvements in Rural Affairs 3, no. 1 (January 1837): 1–10, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Roy Rosenzweig and Elizabeth Blackmar, The Park and the People: A History of Central Park (Ithaca, NY: Cornell University Press, 1992), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Constance Greiff, John Notman, Architect, 1810–1865 (Philadelphia: Athenaeum of Philadelphia, 1979), view on Zotero.
- ↑ John Fanning Watson, Annals of Philadelphia and Pennsylvania in the Olden Time. . . 2 vols. (Philadelphia: E. Thomas, 1857), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Ephraim Chambers, Cyclopaedia, or An Universal Dictionary of Arts and Sciences. . . , 5th edn, 2 vols (London: D. Midwinter et al., 1741–43), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Samuel Johnson, A Dictionary of the English Language: In Which the Words Are Deduced from the Originals and Illustrated in the Different Significations by Examples from the Best Writers, 2 vols. (London: W. Strahan for J. and P. Knapton, 1755), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Philip Miller, The Gardeners Dictionary (1759; repr., New York: Verlag Von J. Cramer, 1969), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Charles Marshall, An Introduction to the Knowledge and Practice of Gardening, 1st American ed., 2 vols. (Boston: Samuel Etheridge, 1799), view on Zotero.
- ↑ J. C. (John Claudius) Loudon, An Encyclopaedia of Gardening; Comprising the Theory and Practice of Horticulture, Floriculture, Arboriculture, and Landscape-Gardening, 4th ed. (London: Longman et al., 1826), view on Zotero.
- ↑ James E. Teschemacher, “Extracts from Foreign Publications,” Horticultural Register, and Gardener’s Magazine 1 (August 1, 1835): 304–9, view on Zotero.
- ↑ Louisa C. Tuthill, History of Architecture, from the Earliest Times; Its Present Condition in Europe and the United States. . . , (Philadelphia: Lindsay and Blakiston, 1848), view on Zotero.
- ↑ A. J. [Andrew Jackson] Downing, A Treatise on the Theory and Practice of Landscape Gardening, Adapted to North America, 4th ed. (1849; repr., Washington, DC: Dumbarton Oaks Research Library and Collection, 1991), view on Zotero.
- ↑ Henry Noel Humphreys, “Notes on Decorative Gardening-Fountains,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 5, no. 5 (November 1850): 208–11, view on Zotero.
- ↑ R. B. L., “On Artificial Rockeries,” Horticulturist and Journal of Rural Art and Rural Taste 6, no. 6 (June 1851): 276–79, view on Zotero.















